
FRSE
Chair in Human Nutrition
- About
-
- Email Address
- lora.heisler@abdn.ac.uk
- Telephone Number
- +44 (0)1224 437446
- Office Address
Foresterhill
AB25 2ZD- School/Department
- School of Medicine, Medical Sciences and Nutrition
Biography
Professor Heisler investigates brain circuits regulating energy homeostasis in an effort to identify new targets amenable to obesity and type 2 diabetes medications. Professor Heisler received her PhD from Tufts University, USA in 1997 and held postdoctoral positions at the University of California, San Francisco USA and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School USA. In 2001, Professor Heisler was promoted to Instructor and set up her laboratory at Harvard. She then relocated her group to the University of Cambridge, UK in 2004 where they worked for the next 10 years. Prof Heisler was a Wellcome Trust Senior Fellow at this time. The Heisler laboratory moved to the Rowett Institute, University of Aberdeen to take advantage of the Institute’s strengths in obesity research, ranging from molecules to man.
News
The MOOMIN (Mechanisms Of Obesity, Metabolism, Insulin Sensitivity and Nutrition) Lab welcomes new postdoctoral fellow Dr Shuwen Mu!
Congratulations Dr Alasdair Leeson-Payne on his first authored publication to be published in Cell Metabolism 2024.
Many congratulations to PhD student Dhamyaa Al Halboosi on her first paper published in Neuropharmacology Dec 2023 entitled "Modulation of GABA release by 5-HT1B receptors: An interplay with AMPA-receptors and voltage-gated calcium channels."
Best wishes to former postdoctoral fellow Dr Pablo Martinez de Morentin who is setting up his new lab at University of Leeds.
Congratulations Matev Arcon for his successful PhD viva!
See Prof Heisler present the lab's latest work at the Keystone 'Obesity Causes and Consequences' conference in Vancouver, Canada Feb 2024.
Sign up to attend the British Society for Neuroendocrinology's annual meeting in Aberdeen 1-3 July 2024 https://www.neuroendo.org.uk/page.php?item_name=BSN+Annual+Meeting+2024
Memberships and Affiliations
- Internal Memberships
-
Director of Research, Rowett Institute
Aberdeen Cardiovascular and Diabetes Centre member
- External Memberships
-
Deputy Editor, Molecular Metabolism
Scientific Advisory Board, Keystone Symposia
Latest Publications
Mesenchymal-specific Alms1 knockout in mice recapitulates metabolic features of Alström syndrome
Molecular Metabolism, vol. 84, 101933Contributions to Journals: ArticlesLoss of GPR75 protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and body fat accumulation
Cell Metabolism, vol. 36, no. 5, pp. 1076-1087Contributions to Journals: ArticlesGLP-1 receptor agonist improves metabolic disease in a pre-clinical model of lipodystrophy
Frontiers in Endocrinology, vol. 15, 1379228Contributions to Journals: ArticlesA brainstem to hypothalamic arcuate nucleus GABAergic circuit drives feeding
Current Biology, vol. 34, no. 8, pp. 1646-1656.e4Contributions to Journals: ArticlesModulation of GABA release by 5-HT1B receptors: An interplay with AMPA-receptors and voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
Neuropharmacology, vol. 241, 109758Contributions to Journals: Articles
Prizes and Awards
Professor Heisler was the recipient of the Outstanding Scientific Achievement Award (OSAA) from the American Diabetes Association. Professor Heisler received the OSAA prize for her research identifying a new type of medication to improve type 2 diabetes. This prestigious award recognises research in diabetes that demonstrates particular independence of thought and originality. Her career scientific contributions include seminal discoveries in the brain control of appetite and blood sugar that demonstrate her innovation.
Professor Heisler commented: “Diabetes is such a widespread problem and it is crucial that we as scientists continue to research this disease in order to find new ways to combat it. It is extremely humbling to be recognised for our contribution to diabetes research. I work alongside many talented colleagues."
Professor Heisler was also the recipient of the Outstanding Scientific Achievement Award from the Obesity Society for her work defining the therapeutic mechanism of a globally prescribed obesity medication.
She has received similar prizes from other international societies and is regularly invited to give Keynote talks at scientific conferences.
- Research
-
Research Overview
Moomin Lab
Mechanisms Of Obesity, Metabolism, Insulin Senstivity and Nutrition

Our research aims to discover and characterise these brain circuits using cutting edge technology with the objective of locating points within the pathway that are amenable to manipulation with manmade (drug) or natural (hormone) substances.
We also examine the impact of diet and body weight on circuit rewiring and mechanisms restore appropriate system connectivity and activity.
The ultimate aim of our research is to identify new treatments for obesity and type 2 diabetes.
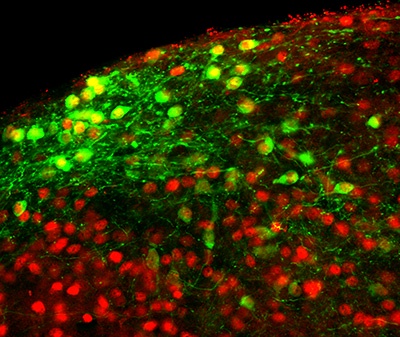

Cells in the brain that impact appetite Our work identifying a new treatment
for type 2 diabetes is on the journal coverCurrent Research
Current projects include:
- Identifying the brain mechanism of action of GLP-1 receptor obesity medications
- Defining how mutations in the orphan receptor GPR75 are protective for the development of obesity, type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease
- Establishing how factors within the brainstem nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) control food intake and body weight
- Defining how the brain controls physical activity and energy expenditure and how this circuitry become disrupted with ageing
- Targeting brain serotonin (5-HT) receptors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Research team:
- Dr Alasdair Leeson Payne - Research fellow
- Dr Akihiro Mori - Research fellow
- Dr Shuwen Mu - Research fellow
- Miss Raffaella Chianese - Laboratory Manager
- Miss Dhamyaa Al-Halboosi - PhD Student
- Mr Matevz Arcon - PhD Student
- Miss Hollie Whyte - MSc Student
- Miss Janvi Ghoricha - MSc Student
- Miss Jessica Christie - MSc Student
Funding and Grants
BBSRC
Diabetes UK
Wellcome Trust
Medical Research Scotland
- Teaching
-
Teaching Responsibilities
Frontiers of Biomedical Science - SM3002
- Publications
-
Page 2 of 3 Results 26 to 50 of 54
Intracerebroventricular Catalase Reduces Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity and Increases Responses to Hypoglycemia in Rats
Endocrinology, vol. 157, no. 12, pp. 4669–4676Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2015-2054
- [OPEN ACCESS] http://aura.abdn.ac.uk/bitstream/2164/7822/1/en_2E2015_2054.pdf
Serotonin engages an anxiety and fear-promoting circuit in the extended amygdala
Nature, vol. 537, pp. 97-101Contributions to Journals: ArticlesChronic Activation of γ2 AMPK Induces Obesity and Reduces β Cell Function
Cell Metabolism, vol. 23, no. 5, pp. 821-836Contributions to Journals: Articles5-HT2Aand 5-HT2C receptors as hypothalamic targets of developmental programming in male rats
Development, vol. 143, no. 8, pp. 401-412Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.138396
- [OPEN ACCESS] http://aura.abdn.ac.uk/bitstream/2164/12806/1/Martin_Gronert_etal_Dev_VOR.pdf
5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors as hypothalamic targets of developmental programming in male rats
Disease Models & Mechanisms, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 401-412Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.023903
- [OPEN ACCESS] http://aura.abdn.ac.uk/bitstream/2164/6125/1/401.full.pdf
Appetite controlled by a cholecystokinin nucleus of the solitary tract to hypothalamus neurocircuit
eLife, vol. 5, 12225Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.12225
- [OPEN ACCESS] http://aura.abdn.ac.uk/bitstream/2164/5670/3/e12225_download.pdf
Sex difference in physical activity, energy expenditure and obesity driven by a subpopulation of hypothalamic POMC neurons
Molecular Metabolism, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 245-252Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2016.01.005
- [OPEN ACCESS] http://aura.abdn.ac.uk/bitstream/2164/5703/1/1_s2.0_S221287781600017X_main.pdf
- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha plays a crucial role in behavioral repetition and cognitive flexibility in mice
Molecular Metabolism, vol. 4, no. 7, pp. 528-536Contributions to Journals: Articles5-Hydroxytryptamine Medications for the Treatment of Obesity
Journal of Neuroendocrinology, vol. 27, no. 6, pp. 389-398Contributions to Journals: Literature Reviews- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12287
A Parabrachial-Hypothalamic Cholecystokinin Neurocircuit Controls Counterregulatory Responses to Hypoglycemia
Cell Metabolism, vol. 20, no. 6, pp. 1030-1037Contributions to Journals: ArticlesLeptin-inhibited PBN neurons enhance responses to hypoglycemia in negative energy balance
Nature Neuroscience, vol. 17, pp. 1744-1750Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3861
5-HT obesity medication efficacy via POMC activation is maintained during aging
Endocrinology, vol. 155, no. 10, pp. 3732–3738Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2014-1223
- [OPEN ACCESS] http://aura.abdn.ac.uk/bitstream/2164/4096/1/5HT_Obesity_Medication.pdf
Distribution of cells responsive to 5-HT6 receptor antagonist-induced hypophagia
Behavioural Brain Research, vol. 266, pp. 201-206Contributions to Journals: ArticlesDevelopmental Programming Mediated by Complementary Roles of Imprinted Grb10 in Mother and Pup
PLoS Biology, vol. 12, no. 2, 1001799Contributions to Journals: ArticlesProfiling of glucose-sensing neurons reveals that ghrh neurons are activated by hypoglycemia
Cell Metabolism, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 596-607Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.09.002
5-HT2C receptor agonist anorectic efficacy potentiated by 5-HT1B receptor agonist coapplication: an effect mediated via increased proportion of pro-opiomelanocortin neurons activated
Journal of Neuroscience, vol. 33, no. 23, pp. 9800-9804Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4326-12.2013
Neuroanatomical characterisation of the expression of the lipodystrophy and motor-neuropathy gene Bscl2 in adult mouse brain
PloS ONE, vol. 7, no. 9, e45790Contributions to Journals: ArticlesBrain glucose sensors play a significant role in the regulation of pancreatic glucose-stimulated insulin secretion
Diabetes, vol. 61, no. 2, pp. 321-328Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.2337/db11-1050
- [OPEN ACCESS] http://aura.abdn.ac.uk/bitstream/2164/5653/1/Diabetes_2012_Osundiji_321_8.pdf
Setting the tone: reactive oxygen species and the control of appetitive melanocortin meurons
Cell Metabolism, vol. 14, no. 5, pp. 573-574Contributions to Journals: Editorials- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.10.004
Neuropeptide Y cells represent a distinct glucose-sensing population in the lateral hypothalamus
Endocrinology, vol. 152, no. 11, pp. 4046-4052Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2011-1307
Leptin does not directly affect CNS serotonin neurons to influence appetite
Cell Metabolism, vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 584-591Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.03.016
Identification of adropin as a secreted factor linking dietary macronutrient intake with energy homeostasis and lipid metabolism
Cell Metabolism, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 468-481Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2008.10.011
5-HT2CRs expressed by pro-opiomelanocortin neurons regulate energy homeostasis
Neuron, vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 582-589Contributions to Journals: ArticlesSerotonin 5-HT2C receptor agonist promotes hypophagia via downstream activation of melanocortin 4 receptors
Endocrinology, vol. 149, no. 3, pp. 1323-1328Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2007-1321
Serotonin 2C receptor agonists improve type 2 diabetes via melanocortin-4 receptor signaling pathways
Cell Metabolism, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 398-405Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2007.10.008
