
In Medieval times, people saw society as divided into three groups,
 called the 'three estates': the nobility (knights, their lords, the king); the
clergy (bishops, abbots, monks, nuns, etc.); and the labourers (everyone else
- see picture right). God must have put people into these estates for a reason,
people thought, and each had a task to perform.
called the 'three estates': the nobility (knights, their lords, the king); the
clergy (bishops, abbots, monks, nuns, etc.); and the labourers (everyone else
- see picture right). God must have put people into these estates for a reason,
people thought, and each had a task to perform.
'God's house is threefold,' a French bishop wrote, 'some pray in it, some fight in it, some work in it.' The labourer had to work to provide food and the other basic things needed to live on. The noblemen, in return for living in much greater comfort than the labourer, was expected to defend the poor and to set a good example in the way he behaved. The clergy, meanwhile, was in charge of the religious life of the community and had to please God by serving Him every day.
So the main purpose of the life of monks and nuns was to serve God through prayer and praise. This meant getting up at midnight for the first service of the day (called Matins) which could last until nearly dawn. The monks and nuns might stand and sing as many as fifty psalms from memory. After Matins came Lauds, then Prime, and so on every few hours throughout the day until Vespers and Compline in the evening.

Monks copying
In between these services - called 'God's Work' - there was barely time for a few hours' sleep, for meals of pottage (thick grain and vegetable soup) or fish (monks or nuns were supposed to eat meat only when they were ill), for work in the garden (monks and nuns grew their own food and often made their own clothes) or copying books.

A richly decorated letter (called an illuminated letter)
Yet many monks and nuns had other duties which meant they could not follow the strict life of prayer all the time.

Nuns looking after people in an 'almshouse', a home for old people
They cared for old people, for the sick, even for lepers, who were not allowed to go near other people as the disease of leprosy was catching. There were over four hundred hospitals in England run by monks and nuns.
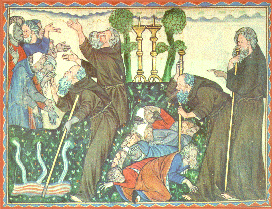
Friars looking after the sick
They ran orphanages and taught boys (and occasionally girls) to read and write. Many monasteries had guest-houses where travellers could spend the night.
There were many different kinds (or 'Orders') of monks and nuns: Benedictines, Cistercians, Dominicans, Franciscans, etc. There wore different clothes and had different rules. (Monks and nuns made vows that they would keep these when they joined the Order.) Some, like the Friars founded by Francis of Assisi, were not supposed to live in monasteries at all, but to go about preaching and to live off what people gave them. There were even soldier-monks like the Templars who went on Crusades to capture the Holy Land from the Muslims.
Some of these Orders became very rich. They owned land and made a great deal of money from selling crops or things that they made (such as beer, liqueurs and perfume). The Cistercian monks of Fountains Abbey in Yorkshire, for example, were sheep-farmers and made a large fortune dyeing and selling their wool.
Not everyone thought it was right for monasteries to be so wealthy, and for abbots and bishops to live like lords, feasting and hunting. People could see that some monks and nuns lived an easy life but not a holy one. Not all of them kept their vows.

A monk stealing some wine