
BS, PhD, FRSB
Senior Lecturer
- Email Address
- a.m.rajnicek@abdn.ac.uk
- Telephone Number
- +44 (0)1224 437514
- Office Address
- School/Department
- School of Medicine, Medical Sciences and Nutrition
Qualifications
- BSc Biology1984 - Marygrove College (Detroit, MI USA)
- PhD Developmental Biology1990 - Purdue University (W Lafayette, IN USA)Thesis title: Effects of electric fields on wound healing and directed neurite growth
Memberships and Affiliations
- Chair: School of Medicine, Medical Sciences and Nutrition, Staff Student Liaison Committee, Level 2 courses (2008-present)
- Senior Personal Tutor: School of Medicine ,Medical Sciences and Nutrition (2021-present)
- Co-lead, Co-founder: The IDEALL Group for Equality and Diversity (2016-2021)
- Member: Institute of Medical Sciences Equality, Diversity and Inclusion Committee (2016-present)
- Elected Member: University Senate (2012-2016; 2016-2020; 2023-2026)
- Member: Self Assessment Team, Institute of Medical Sciences Athena Swan Application (2015-2019)
Senior Journal Editor/Media Editor: Bioelectricity (2019-present)(https://home.liebertpub.com/publications/bioelectricity/647)
External examiner: Glasgow University, Molecular and Cellular Biology/Biotechnology/Bioengineering undergraduate degrees (2017-2021)
Fellow: Royal Society of Biology (FRSB)
Member: Society for Neuroscience
Member: British Society for Cell Biology
Member: Scottish Developmental Biology Group
Member: American Society for Cell Biology
Vice Chair: Gordon Research Conference on Bioelectrochemistry (2006)
Chair: Gordon Research Conference on Bioelectrochemistry (2008)
Board Member: Bioelectromagnetics Society (2008-2011)
Council Member: Bioelectrochemical Society (2009-2013)
Prizes and Awards
Yasuda Award for Excellence in Biomedical Research (Jan 2000) Society for Physical Regulation in Biology and Medicine.
Research Overview
I am interested in the process by which cells use environmental conditions as guidance cues during development, wound healing and regeneration. My work has potential applications in tissue engineering and for devising clinical strategies to aid wound healing and nervous system repair.
Guiding cells by DC electric fields
Cells exist within a naturally-occuring electric field, which results from the normal ion transport properties of polarized epithelia. My research addresses the question of how cells use the electric field as a cue to direct cell migration and orientation.
Guiding cells by small substratum contours
The physical shape of the extracellular environment is usually not considered in the context of directional cell migration. However, cells migrate along parallel substratum features on the scale of tens to hundreds of nanometers, which mimic the size of naturally ocurring features (such as individual collagen fibrils or oriented neuronal fibers). I am interested in the process by which individual cells sense very small substratum features and how they translate the cues subsequently into directed migration.
Establishing a guidance heirarchy
Since electric fields and variation in substratum shape co-exist in vivo another interest is to determine the hierarchy of directional cues and the mechanisms that allow the cues to be selected/integrated by individual cells.
Rho GTPases and growth cone guidance by an electric field
The Rho GTPases Rac, Rho and Cdc42 regulate cytoskeletal dynamics spatially and therefore control cell shape and the direction of cell migration. We have shown that Rho GTPase-mediated cytoskeletal dynamics are essential for growth cone guidance by an electric field (Rajnicek et al., 2006 Journal of Cell Science 119:1723-1735; Rajnicek et al. 2006 Journal of Cell Science 119: 1736-45).
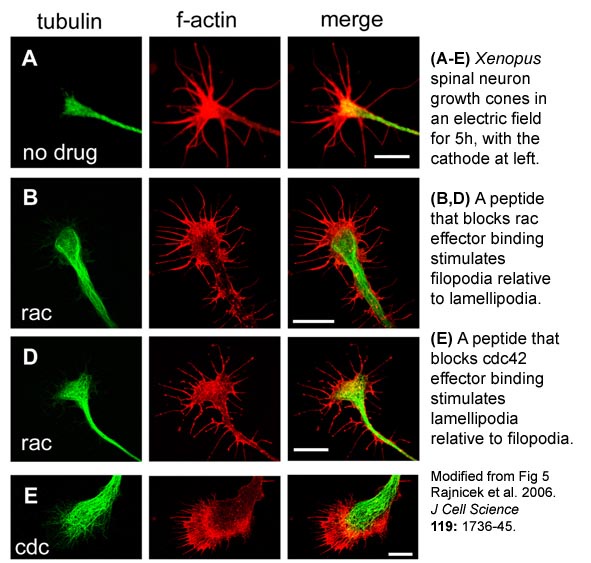
Current Research
Growth cone guidance by substratum grooves
Growth cones are exquititely sensitive to substratum features on the scale of tens of nanometers deep but not all types of growth cones respond in the same way to identical features. For example, embryonic rat hippocampal axons align at a right angle to a series of parallel grooves 130 nm deep and 1 um across but Xenopus spinal neuron growth cones migrate parallel to the same grooves. I am currently exploring the intracellular mechanisms growth cones use to detect small substratum features, including roles for Rho GTPases and the transcription factor Pax-6 (collaboration with Martin Collinson and Derryck Shewan, School of Medical Sciences, University of Aberdeen).
Guidance of epithelial cells by substratum nanotopograpy and electric fields is controlled by a rho/cdc42 switch
Cells migrating to re-epithelialise a wound in the cornea migrate over non-planar surfaces within the context of a wound-induced DC electric field. We have shown that corneal epithelial cells migrate parallel to nano-scale substratum grooves and that on planar quartz they migrate toward the cathode of a DC electric field. By simultaneously challenging corneal cells with co-presented substratum grooves and an electric field oriented orthogonally we determined that the electric field was a more potent directional cue and that a cdc42/rho switch controls electrical/contact guidance priority. This is relevant to the design of future therapies to aid wound healing as well as the basic mechanism for how cells sort/select/integrate simultaneous directonal guidance cues present in the normal extracellular environment.
Collaborations
Aberdeen- Prof Nieves Casan-Pastor, Dr W Huang, Dr D Shewan, Dr M Collinson, Dr H Wilson, Prof M Delibegovic
Funding and Grants
IMS Spinal Research Fund -PhD Studentship "Electrical Control of Nerve Cell Growth"
School of Medical Sciences -PhD Studentship "The transcription factor Pax6 and neuronal guidance" (with M Collinson and D Shewan)
European Commission Specific Targeted Research or Innovation Project - "Development of a Bioelectrochemical device for CNS repair" (NERBIOS) ~£220,000 (with C.D. McCaig)
BBSRC - Genetic control of epithelial cell migration and wound healing physiology (with M Collinson, C McCaig and M.Zhao) ~£643,000.
Programmes
- Undergraduate, 4 year, September start
Programme Lead
Courses
Teaching Responsibilities
Course Coordinator:
SM3002- Frontiers of Biomedical Sciences
PY4302 (AN4301)- Developmental Neuroscience (with Anatomy)
AN4002 (AN4003)- Brain Function and Malfunction (with Anatomy)
BM3804- Neuroscience Research Topics
Non-course Teaching Responsibilities
Senior Personal Tutor for School of Medicine, Medical Sciences and Nutrition (undergraduates)
Personal Tutor and related pastoral care for undergraduates
Industrial Placement Tutor
Chair Level 2 undergraduate Staff Student Liaison Committee
Page 1 of 1 Results 1 to 69 of 69
Bioelectricity Buzz: Recent Bioelectricity-Related Articles Selected by Ann M. Rajnicek, Media Editor of Bioelectricity
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 86-93Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2025.0012
Recent Bioelectricity-Related Articles Selected by Ann M. Rajnicek, Media Editor of Bioelectricity
Rajnicek, A.BioelectricityContributions to Journals: ArticlesBioelectricity Buzz
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 6, no. 3Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2024.0035
Bioelectricity Buzz
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 221–228Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2024.0035
Bioelectricity Buzz
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 143-149Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2024.0024
Wireless control of nerve growth using bipolar electrodes: a new paradigm in electrostimulation
Rajnicek, A. M., Casañ-Pastor, N.Biomaterials Science, vol. 12, no. 9, pp. 2180-2202Contributions to Journals: ArticlesBioelectricity Buzz
Rajnicek, A. M.Bioelectricity, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 57-64Contributions to Journals: Comments and Debates- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2024.0012
- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
Bioelectricity Buzz
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 57–64Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2024.0012
Ion Channels As Emerging Metabolic Regulators and Therapeutic Targets in Osteoarthritis: Nav1.7 As a Recent Exemplar
Mobasheri, A., Matta, C., Giles, W., Rajnicek, A. M., Ivanavicius, S.Bioelectricity, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 54-56Contributions to Journals: Review articlesBioelectricity Buzz
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 318-325Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2023.0046
Bioelectricity Buzz
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 220Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2023.0037
Bioelectricity Buzz
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 139-146Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2023.0021
Bioelectricity Buzz
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 65Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2023.0010
Bioelectricity Buzz
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 268-273Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2022.0037
Effectiveness of biomaterial-based combination strategies for spinal cord repair – a systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical literature
Guijarro Belmar, A., Varone, A., Rugema Baltzer, M., Kataria, S., Tanriver-Ayder, E., Watzlawick, R., Sena, E., Cunningham, C., Rajnicek, A., Macleod, M. R., Huang, W., Currie, G. L., McCann, S. K.Spinal Cord, vol. 60, no. 12, pp. 1041-1049Contributions to Journals: Review articlesBioelectricity Buzz
Rajnicek, A. M.Bioelectricity, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 178-185Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2022.0026
- [OPEN ACCESS] http://aura.abdn.ac.uk/bitstream/2164/19833/1/Rajnicek_Bioelectricity_Buzz_AAM.pdf
- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
Bioelectricity Buzz
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 126-132Contributions to Journals: ArticlesRecent Bioelectricity-Related Articles Selected by Ann M. Rajnicek, Media Editor of Bioelectricity
Rajnicek, A. M.Bioelectricity, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 59-64Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2022.0002
- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
Analyzing Electricity In The Human Body, And How Doctors May Be Able To Harness It For Medical Treatment
Rajnicek, A.Non-textual Forms: Digital or Visual Products- [ONLINE] http://apple.co/30PvU9C
Nanostructured electroactive materials with large charge capacity: Direct field electrostimulation through connected and non-connected electrodes
Rajnicek, A., Suñol, C., Casañ-Pastor, N.Engineering Biomaterials for Neural Applications: Targeting Traumatic Brain and Spinal Injury. López-Dolado, E., Concepción Serrano, M. (eds.). Springer International Publishing AG, pp. 99-125, 27 pagesChapters in Books, Reports and Conference Proceedings: ChaptersRecent, bioelectricity-related articles selected by Ann M. Rajnicek, Media Editor of Bioelectricity
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 294-299Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2021.0035
Recent, bioelectricity-related articles selected by Ann M. Rajnicek, Media Editor of Bioelectricity
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 229-234Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2021.0023
Recent, bioelectricity-related articles selected by Ann M. Rajnicek, Media Editor of Bioelectricity
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 147-153Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2021.0018
Recent, Bioelectricity-Related Articles Selected by Ann M. Rajnicek, Media Editor of Bioelectricity: Bioelectricity, volume 3
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 101-106Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2021.0003
Methodology of Research and Applications of Electric Fields
Lin, F., Rajnicek, A., Zhao, M.Bioelectricity, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 320Contributions to Journals: Editorials- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2020.0050
- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
Recent Bioelectricity-Related Articles Selected by Ann M. Rajnicek, Media Editor of Bioelectricity
Rajnicek, A. M.Bioelectricity, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 405-410Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2020.0049
- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
Recent Bioelectricity-Related Articles Selected by Ann M. Rajnicek, Media Editor of Bioelectricity: Bioelectricity, volume 2
Rajnicek, A. M. (ed.)Bioelectricity, vol. 2, no. 4Contributions to Journals: Editorials- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2020.0049
Recent bioelectricity-related articles selected by Ann M Rajnicek, Media Editor of Bioelectricity
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 305-309Contributions to Journals: Editorials- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2020.0037
Recent Bioelectricity-related articles selected by Ann M Rajnicek, Media Editor of Bioelectricity
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 198-202Contributions to Journals: Editorials- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2020.29019.ara
In Memorium: Richard Borgens, 1946-2019
Levin, M., Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 205Contributions to Journals: Editorials- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2020.29018.mle
Recent Bioelectricity-related articles selected by Ann M. Rajnicek, Media Editor
Rajnicek, A.Bioelectricity, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 59-62Contributions to Journals: Editorials- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2020.0004
Physiological strength electric fields modulate human T cell activation and polarisation
Arnold, C. E., Rajnicek, A., Hoare, J. I., Pokharel, S. M., McCaig, C., Barker, R. N., Wilson, H. M.Scientific Reports, vol. 9, 17604Contributions to Journals: ArticlesRoles for IFT172 and primary cilia in cell migration, cell division and neocortex development
Pruski, M., Hu, L., Yang, C., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, L., Huang, Y., Rajnicek, A. M., St Clair, D., McCaig, C. D., Lang, B., Ding, Y.Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, vol. 7, 287Contributions to Journals: ArticlesElectric field gradients and bipolar electrochemistry effects on neural growth: A finite element study on immersed electroactive conducting electrode materials
Abad, L., Rajnicek, A. M., Casañ-Pastor, N.Electrochimica Acta, vol. 317, pp. 102-111Contributions to Journals: ArticlesElectrical Stimulation Directs Migration, Enhances and Orients Cell Division and Upregulates the Chemokine Receptors CXCR4 and CXCR2 in Endothelial Cells
Cunha, F., Rajnicek, A. M., McCaig, C. D.Journal of Vascular Research, vol. 56, no. 1, pp. 39-53Contributions to Journals: ArticlesThe Bioelectricity revolution: a discussion among the founding associate editors
Spencer Adams, D., Djamgoz, M., Levin, M., Zhao, M., Rajnicek, A., Nuccitelli, R., Archangeli, A., Kramer, R., Bates, E. A.Bioelectricity, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 8-15Contributions to Journals: Editorials- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/bioe.2018.28999.rtl
Controlling Nerve Growth with an Electric Field Induced Indirectly in Transparent Conductive Substrate Materials
Rajnicek, A. M., Zhao, Z., Moral-Vico, J., Cruz, A., McCaig, C., Casan-Pastor, N.Advanced Healthcare Materials, vol. 7, no. 17, 1800473Contributions to Journals: ArticlesA refined rat primary neonatal microglial culture method that reduces time, cost and animal use
Georgieva, M., Leeson-Payne, A., Dumitrascuta, M., Rajnicek, A., Malcangio, M., Huang, W.Journal of Neuroscience Methods, vol. 304, pp. 92-102Contributions to Journals: ArticlesSilkworm silk biomaterials for spinal cord repair: promise for combinatorial therapies
Varone, A., Rajnicek, A. M., Huang, W.Neural Regeneration Research, vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 809-810Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.232471
- [OPEN ACCESS] http://aura.abdn.ac.uk/bitstream/2164/10502/1/NeuralRegenResArticle.pdf
The potential of Antheraea pernyi silk for spinal cord repair
Varone, A., Knight, D., Lesage, S., Vollrath, F., Rajnicek, A. M., Huang, W.Scientific Reports, vol. 7, pp. 1-10Contributions to Journals: ArticlesTiO2 surfaces support neuron growth during electric field stimulation
Canillas, M., Moreno, B., Chinnaro, E., Rajnicek, A. M.Materials Science and Engineering C, vol. 79, pp. 1-8Contributions to Journals: ArticlesRequirement of Pax6 for the integration of guidance cues in cell migration
Arocena, M., Rajnicek, A. M., Collinson, J. M.Royal Society Open Science, vol. 4, 170625Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.170625
- [OPEN ACCESS] http://aura.abdn.ac.uk/bitstream/2164/9465/1/Requirement_of_Pax6_for.pdf
The core planar cell polarity gene, Vangl2, directs adult corneal epithelial cell alignment and migration
Findlay, A. S., Panzica, D. A., Walczysko, P., Holt, A. B., Henderson, D. J., West, J. D., Rajnicek, A. M., Collinson, J. M.Royal Society Open Science, vol. 3, no. 10, 160658Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.160658
- [OPEN ACCESS] http://aura.abdn.ac.uk/bitstream/2164/7592/1/160658.full.pdf
Contact-mediated control of radial migration of corneal epithelial cells
Walczysko, P., Rajnicek, A. M., Collinson, J. M.Molecular vision, vol. 22, pp. 990-1004Contributions to Journals: ArticlesElectric fields are novel determinants of human macrophage functions
Hoare, J. I., Rajnicek, A. M., McCaig, C. D., Barker, R. N., Wilson, H. M.Journal of Leukocyte Biology, vol. 99, no. 6, pp. 1141-1151Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.3A0815-390R
Neuronal Growth Cone Guidance by Physiological DC Electric Fields
Rajnicek, A. M.The Physiology of Bioelectricity in Development, Tissue Regeneration and Cancer. 1st edition. CRC Press, pp. 201-232, 32 pagesChapters in Books, Reports and Conference Proceedings: Chapters- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1201/b10799-15
- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
The ciliary GTPase Arl13b regulates cell migration and cell cycle progression
Pruski, M., Rajnicek, A., Yang, Z., Clancy, H., Ding, Y., McCaig, C. D., Lang, B.Cell Adhesion & Migration, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 393-405Contributions to Journals: ArticlesElectric fields: a novel non-chemical regulator of human macrophage function
Hoare, J. I., Barker, R. N., Mccaig, C. C., Rajnicek, A., Wilson, H. M.Immunology, vol. 143, no. Suppl 2, pp. 96-96Contributions to Journals: Abstracts- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.12406
Ti4O7 used as electrode in biomedicine and for electrochemical study of scavenging mechanism
Canillas, M., Rajnicek, A., Rosero, C., Chinarro, E., Moreno, B.Chapters in Books, Reports and Conference Proceedings: Conference Proceedings- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.493-494.896
- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
Interaction between hedgehog signalling and PAX6 dosage mediates maintenance and regeneration of the corneal epithelium
Kucerova, R., Dorà, N., Mort, R. L., Wallace, K., Leiper, L. J., Lowes, C., Neves, C., Walczysko, P., Bruce, F., Fowler, P. A., Rajnicek, A. M., McCaig, C. D., Zhao, M., West, J. D., Collinson, J. M.Molecular vision, vol. 18, pp. 139-150Contributions to Journals: ArticlesThe role of electrical signals in murine corneal wound re-epithelialization
Kucerova, R., Walczysko, P., Reid, B., Ou, J., Leiper, L. J., Rajnicek, A. M., Mccaig, C. D., Zhao, M., Collinson, J. M.Journal of Cellular Physiology, vol. 226, no. 6, pp. 1544-1553Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.22488
Electric field effects on neuronal growth cone guidance
Rajnicek, A. M.The Physiology of Bioelectricity in Development, Tissue Repair, Tissue Regeneration and Cancer: Weak Electric Field Effects on Cells, Subcellular systems and Tissues. Pullar, C. E. (ed.). CRC PressChapters in Books, Reports and Conference Proceedings: ChaptersA role for L-α-lysophosphatidylinositol and GPR55 in the modulation of migration, orientation and polarization of human breast cancer cells
Ford, L. A., Roelofs, A. J., Anavi-Goffer, S., Mowat, L., Simpson, D. G., Irving, A. J., Rogers, M. J., Rajnicek, A. M., Ross, R. A.British Journal of Pharmacology, vol. 160, no. 3, pp. 762-771Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00743.x
Electrical dimensions in cell science
McCaig, C. D., Song, B., Rajnicek, A. M.Journal of Cell Science, vol. 122, no. 23, pp. 4267-4276Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.023564
Chronic wound state exacerbated by oxidative stress in Pax6+/-aniridia-related keratopathy
Ou, J., Walczysko, P., Kucerova, R., Rajnicek, A. M., McCaig, C. D., Zhao, M., Collinson, J. M.The Journal of pathology, vol. 215, no. 4, pp. 421-430Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/path.2371
Alignment of corneal and lens epithelial cells by co-operative effects of substratum topography and DC electric fields
Rajnicek, A. M., Foubister, L. E., McCaig, C. D.Biomaterials, vol. 29, no. 13, pp. 2082-2095Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.01.015
Prioritising guidance cues: Directional migration induced by substratum contours and electrical gradients is controlled by a rho/cdc42 switch
Rajnicek, A. M., Foubister, L. E., McCaig, C. D.Developmental Biology, vol. 312, no. 1, pp. 448-460Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.YDBIO.2007.09.051
Hardwiring the Brain: Endocannabinoids Shape Neuronal Connectivity
Berghuis, P., Rajnicek, A. M., Morozov, Y. M., Ross, R. A., Mulder, J., Urban, G. M., Morony, K., Marsicano, G., Matteoli, M., Canty, A., Irving, A. J., Katona, I., Yanagawa, Y., Rakic, P., Lutz, B., Mackie, K., Harkany, T.Science, vol. 316, no. 5828, pp. 1212-1216Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.1137406
Growth cone steering by a physiological electric field requires dynamic microtubules, microfilaments and Rac-mediated filopodial asymmetry
Rajnicek, A. M., Foubister, L. E., McCaig, C. D.Journal of Cell Science, vol. 119, pp. 1736-1745Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02897
Temporally and spatially coordinated roles for Rho, Rac, Cdc42 and their effectors in growth cone guidance by a physiological electric field.
Rajnicek, A. M., Foubister, L. E., McCaig, C. D.Journal of Cell Science, vol. 119, pp. 1723-1735Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02896
Controlling cell behaviour electrically: current views and future potential
McCaig, C. D., Rajnicek, A. M., Song, B., Zhao, M.Physiological Reviews, vol. 85, no. 3, pp. 943-978Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00020.2004
Directing cell shape and migration by topographic and electrical signals
Rajnicek, A. M.European Cells and Materials, vol. 4, no. SUPPL. 2, pp. 30-31Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
Has electrical growth cone guidance found its potential?
McCaig, C. D., Rajnicek, A. M., Song, B., Zhao, M.Trends in Neurosciences, vol. 25, no. 7, pp. 354-359Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-2236(02)02174-4
The direction of neurite growth in a weak DC electric field depends on the substratum: Contributions of adhesivity and net surface charge
Rajnicek, A. M., Robinson, K. R., McCaig, C. D.Developmental Biology, vol. 203, no. 2, pp. 412-423Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/dbio.1998.9039
- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
Contact guidance of CNS neurites on grooved quartz: Influence of groove dimensions, neuronal age and cell type
Rajnicek, A. M., Britland, S., McCaig, C. D.Journal of Cell Science, vol. 110, no. 23, pp. 2905-2913Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
Guidance of CNS growth cones by substratum grooves and ridges: Effects of inhibitors of the cytoskeleton, calcium channels and signal transduction pathways
Rajnicek, A. M., McCaig, C. D.Journal of Cell Science, vol. 110, no. 23, pp. 2915-2924Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
Electric fields induce curved growth of Enterobacter cloacae, Escherichia coli, and Bacillus subtilis cells: Implications for mechanisms of galvanotropism and bacterial growth
Rajnicek, A. M., McCaig, C. D., Gow, N. A.Journal of Bacteriology, vol. 176, no. 3, pp. 702-713Contributions to Journals: Articles- [ONLINE] DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.176.3.702-713.1994
- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
Growing Nerves in an Electric Field
McCaig, C. D., Allan, D., Erskine, L., Rajnicek, A. M., Stewart, R.NeuroProtocols, vol. 4, pp. 134-141Contributions to Journals: Literature ReviewsBacterial galvanotropism: mechanisms and applications.
Rajnicek, A. M.Science Progress, vol. 77 ( Pt 1-2), pp. 139-151Contributions to Journals: Review articles- [ONLINE] View publication in Scopus
