CSF
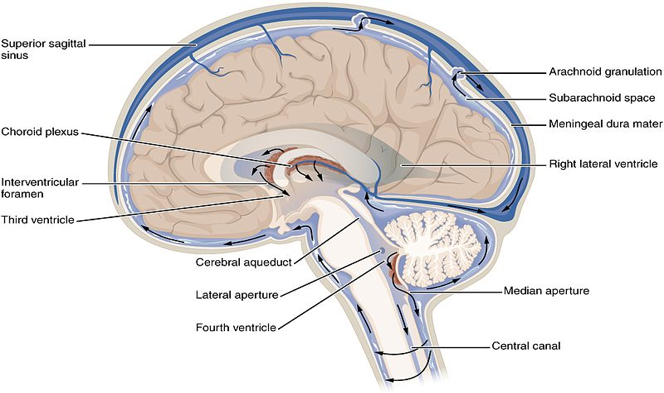
CSF is a clear, proteinaceous fluid that bathes the CNS. CSF has a number of functions. It protects the brain from damage by "buffering" the brain, it excretes waste products e.g. harmful metabolites or drugs and it transports hormones to areas of the brain.
There is around 150ml of CSF circulating at any given moment. ~17% of this volume is located in the ventricles and the remaining in the cisterns and subarachnoid space.
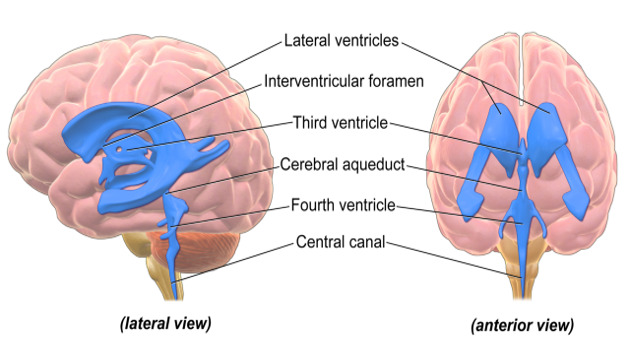
CSF is produced by specialised vascular tissue called choroid plexuses. The choroid plexuses are located in the lateral ventricles, third ventricle and fourth ventricle.
From the lateral ventricles, CSF flows through the right and left foramen of Munro (interventricular foramen) into the third ventricle. Next, it flows through the aqueduct of Sylvius into the fourth ventricle. The 4th ventricle is anterior to the cerebellum.
CSF may exit the foramen of Luschka laterally or the foramen of Magendie medially into the subarachnoid space. When CSF passes through the foramen of Magendie this results in filling of the spinal subarachnoid space. When CSF passes through the foramen of Luschka this results in filling of the subarachnoid space of the cisterns and the cerebral cortex.
CSF is reabsorbed through outpouchings into the superior sagittal sinus called arachnoid granulations. This occurs through a pressure dependent gradient.
