Cromones
Examples
- Sodium Cromoglicate
- Nedocromil sodium
Indications
- Prophylaxis of asthma in children, they are less effective than prophylaxis with corticosteroids. Rarely used in adults.
- Prophylaxis of exercise induced asthma.
- Prophylaxis against allergic rhinitis and allergic conjunctivitis. Cromones can be bought over the counter for treating these conditions
- Used in the management of food allergy when the allergy is difficult to treat by avoidance alone.
- Used as eye drop for eye hayfever symptoms.
Contraindications
Cromones are of no benefit in:
- Acute bronchoconstriction
- Anaphylaxis
- Discontinue if eosinophilic pneumonia occurs
Mechanism
Cromones provide symptomatic relief in allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis. They work by stabilising the mast cell membrane, thus reducing the release of histamines and other messenger molecules. This leads to the reduction of allergic responses.
Cromones have an anti-inflammatory effect in some patients, partially in children, however it is not possible to predict who will respond to treatment. The mechanism of action for reducing inflammation is not well understood, and various theories have been postulated.
Cromones may reduce the frequency and severity of asthma attacks when used in combination with inhaled β2 agonists and inhaled steroids.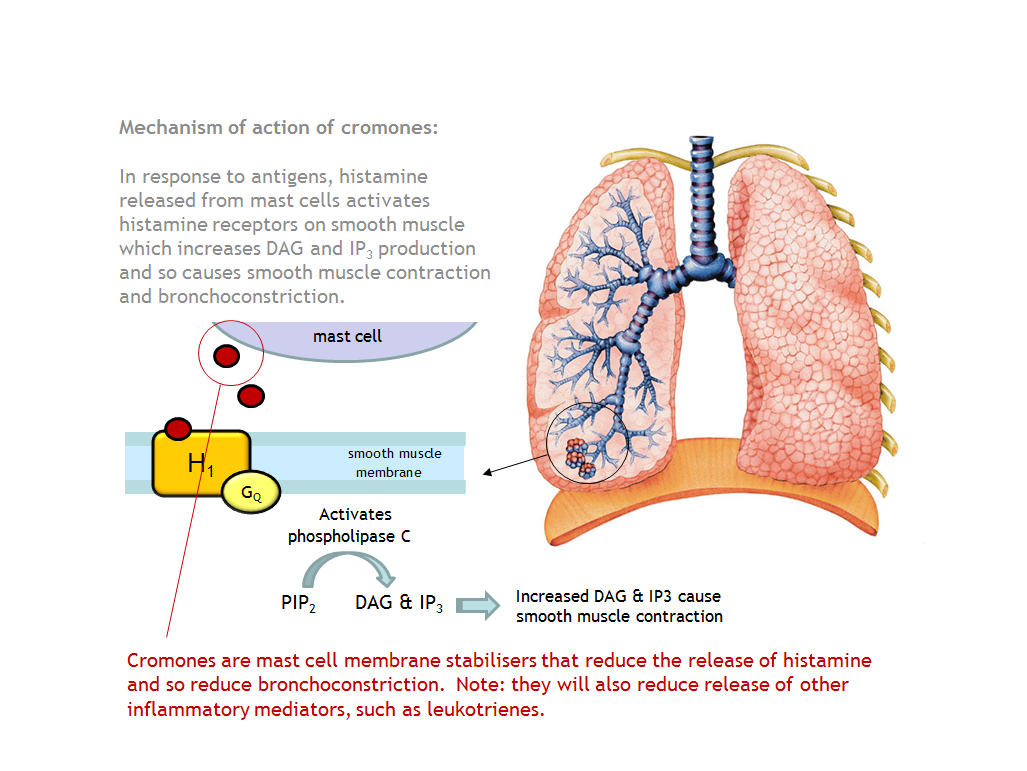
Cromones have an anti-inflammatory effect in some patients, partially in children, however it is not possible to predict who will respond to treatment. The mechanism of action for reducing inflammation is not well understood, and various theories have been postulated.
Cromones may reduce the frequency and severity of asthma attacks when used in combination with inhaled β2 agonists and inhaled steroids.

Administration
Inhaled - in powder form or by nebulised solution. Cromones are given as regular therapy. It may take several weeks before improvement in symptoms are seen.
Topical - Sodium cromoglicate eye drops
Topical - Sodium cromoglicate eye drops
Adverse Reactions
Common
- A bitter taste left in the mouth
- Some preparations of cromones contain benzalkonium chloride and some patients may be allergic to this substance
- With Nedocromil Sodium: Abdominal Pain, dyspepsia, nausea, pharyngitis, vomiting.
- Hypersensitivity reaction in the upper airways, urticaria and anaphylaxis
- Paradoxical broncho-constriction
Interactions
No important drug interactions have been identified.
Education
Ensure the patient understands that cromones are a prophylactic treatment, also referred to as a 'preventer' and they should not be used in the treatment of acute bronchospasm. Ensure your patient is being treated with a β2 agonist concurrently.
Ensure that the patent knows how to use an inhaler device (+/- spacer) correctly. Ask them to demonstrate how to use it.
All patents with asthma require an annual asthma review, with either a doctor or asthma nurse specialist.
Withdrawal from cromones should be done gradually over a week – abrupt cessation may bring about asthmatic symptoms.
Ensure that the patent knows how to use an inhaler device (+/- spacer) correctly. Ask them to demonstrate how to use it.
All patents with asthma require an annual asthma review, with either a doctor or asthma nurse specialist.
Withdrawal from cromones should be done gradually over a week – abrupt cessation may bring about asthmatic symptoms.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: Cromones have very poor gastrointestinal absorption therefore they are administered by inhalation as an aerosol, powdered form or nebulised solution for respiratory disease, or topically. This results in approximately 10% systemic absorption.
