Antimuscarinics
Examples
- Ipratropium
- Tiotropium
- Aclidinium Bromide
- Umeclidinium
Indications
Bronchodilatory muscarinic receptor antagonists are used in:
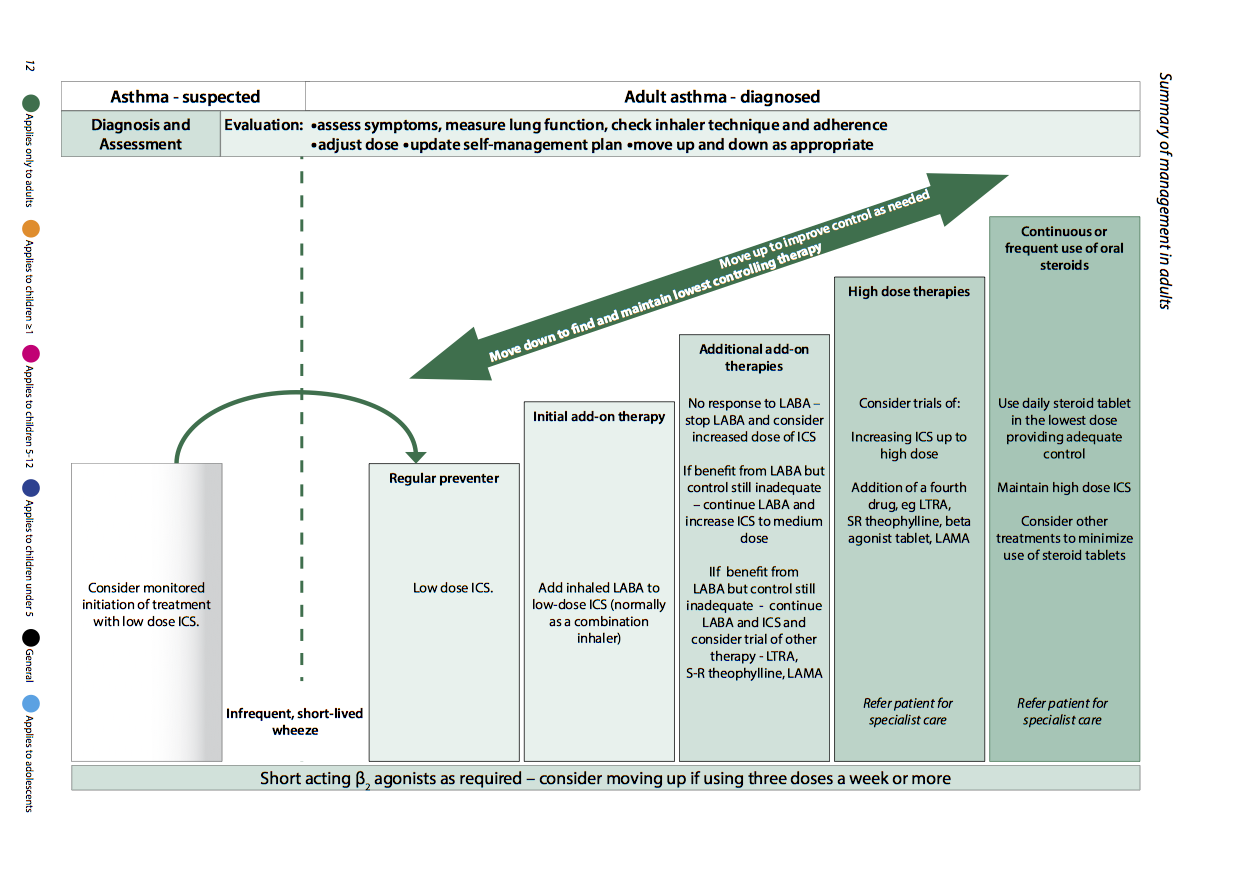
- Treatment of acute bronchospasm (only in combination with β2 agonists). Muscarinic antagonists should not be used alone in acute asthma/COPD because they take more time to act and are less effective than β2 agonists
- Treatment of chronic asthma
- Treatment of COPD, symptomatic relief

Contraindications
Caution
- Patients susceptible to acute angle closure glaucoma; an adverse effect of muscarinic antagonists is a rise in intraocular pressure, this may precipitate acute angle closure glaucoma.
- Patients with bladder outflow obstruction and prostatic hyperplasia; an adverse effect of muscarinic receptor antagonists is relaxation of the bladder which causes urinary retention. In a patient with any degree of bladder outflow obstruction there is a risk of developing acute urinary retention.
- Patients with myasthenia gravis; administration of muscarinic receptor antagonists may cause deterioration in symptoms.
Mechanism
Parasympathetic stimulation causes the release of acetylcholine from the post ganglionic parasympathetic nerve endings, which then acts on cholinergic (muscarinic) receptors, specifically M3 receptors, causing the parasympathetic effect of broncho-constriction.
Muscarinic antagonists competitively inhibit cholinergic receptors on bronchial smooth muscle. They block the action of acetylcholine on the nerve endings therefore inhibiting the parasympathetic effect. This results in dilatation of the airways.

See:
Autonomic and neuromuscular physiology 1 - 2 Dr Davies
And:
Autonomic and neuromuscular pharmacology Dr Rod Scott, science for medicine
Administration
Muscarinic antagonists are administered by Inhalation:
- MDI (metered dose inhaler) +/- large volume spacer device, administration via a spacer reduces systemic exposure and increases the proportion delivered to the lungs
- Nebulisation (care should be taken to ensure a well fitted mask to avoid deposition around the eyes)
Adverse Reactions
Muscarinic receptor antagonists are highly polar molecules and are usually administered by aerosol inhalation. As a result they are not well absorbed into the systemic circulation and hence have little action at muscarinic receptors other than those found in the bronchi. This results in few unwanted effects.
Antagonism of the parasympathetic pathway at muscarinic receptors may lead to adverse effects on other glandular and smooth muscle (note antagonists are not selective and will block all three types of muscarinic receptor – M1, M2 and M3). If the parasympathetic pathway in these tissues is blocked this will result in unopposed sympathetic activity on the tissues, causing classic anticholinergic side effects: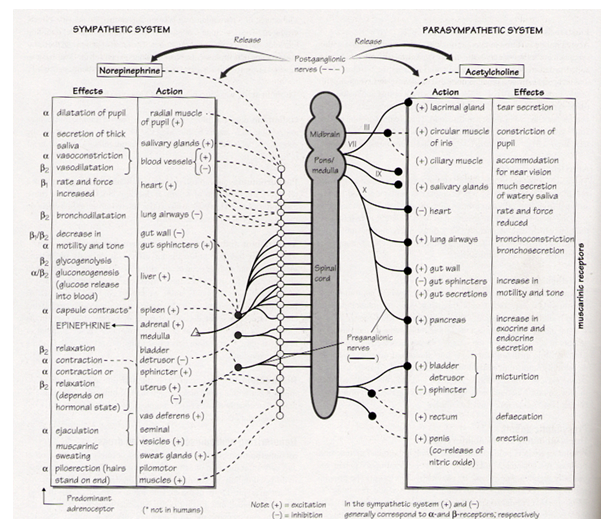
Antagonism of the parasympathetic pathway at muscarinic receptors may lead to adverse effects on other glandular and smooth muscle (note antagonists are not selective and will block all three types of muscarinic receptor – M1, M2 and M3). If the parasympathetic pathway in these tissues is blocked this will result in unopposed sympathetic activity on the tissues, causing classic anticholinergic side effects:
- Dilated pupils
- Blurred vision
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Headache
- Urinary retention / difficulty micturating
- Tachycardia
- Hypotension

Interactions
Care must be taken if prescribing other anticholinergic drugs. This may potentiate the systemic effects of the inhaled muscarinic antagonists.
Education
Muscarinic receptor antagonists are available in combination inhalers with β2 agonists, these inhalers are convenient, but should only be used if the patient requires both drugs regularly.
Ensure that the patent knows how to use an inhaler device (+/- spacer) correctly. Ask them to demonstrate how to use it.
All patients with asthma or COPD require regular review, with either a doctor or asthma nurse specialist.
Ensure that the patent knows how to use an inhaler device (+/- spacer) correctly. Ask them to demonstrate how to use it.
All patients with asthma or COPD require regular review, with either a doctor or asthma nurse specialist.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: The bioavailability of the drug when administered by the inhaled route is 5%.
Ipratropium effects are maximum 30-60 minutes after use, with an action duration of 3 to 6 hours, and with 3 uses a day can maintain bronchodilation.
Ipratropium effects are maximum 30-60 minutes after use, with an action duration of 3 to 6 hours, and with 3 uses a day can maintain bronchodilation.
Other Systems
