Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
Examples
- Citalopram
- Fluoxetine
- Paroxetine
- Sertraline
Indications
- Depressive illness
- Panic disorder
- Obsessive compulsive disorder
- Anxiety disorders
Contraindications
Contraindications
- Mania
- Epilepsy, cardiac disease, diabetes mellitus, susceptibility to angle closure glaucoma, history of mania or bleeding disorders, children under 18
Mechanism
Serotonin is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a role in regulation of mood. SSRIs selectively inhibit the reuptake of the monoamine serotonin (5-HT) within the synapse. The prolongation of the presence of serotonin in the synapse causes an upregulation of its effects on the postsynaptic neuron. However, it is not clear that this mechanism is the full explanation of anti-depressant effects.
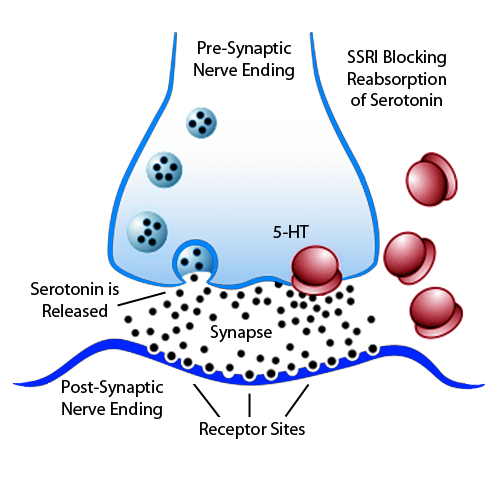
Diagram showing mechanism of action of SSRIs; by blocking reuptake of serotonin at the presynaptic membrane, concentration is increased at the postsynaptic nerve terminal membrane.
Administration
Oral
Adverse Reactions
These drugs are usually well tolerated and side effects are less troublesome than with other anti-depressants.
- Gastro-intestinal effects
- Insomnia
- Sexual dysfunction
- Hypersensitivity reactions including rash
- Mild anti-cholinergic side effects are seen so worsening of symptoms in glaucoma or urinary retention can occur
- Serotonin syndrome is seen, but usually only if these drugs are combined with others that increase serotonin levels (i.e. combination antidepressant therapy) - symptoms include diarrhoea, tremor, shivering, clonus, hyper-reflexia as well as hyperthermia, delirium, agitation, anxiety, hypertension, tachycardia)
- Increase in suicidal thoughts (and behaviour) has sometimes been noted in the first weeks after commencing treatment
- SIADH can occur causing hyponatraemia
- Withdrawal reactions may occur and include gastro-intestinal disturbances, headache, anxiety, dizziness, sleep disturbances. These drugs should therefore be dicontinued gradually, not abruptly.
Interactions
- SSRIs are associated with an increase in bleeding, particularly if given with NSAIDs or aspirin
- There is an increased risk of seizures / serotonin syndrome if used with tramadol
- Drugs of abuse such as amphetamines, cocaine and LSD increase the risk of serotonin syndrome. This also occurs with prescribed medicines such as triptans and silbutramine)
- Interactions occur with other psychiatric drugs such as tricyclics and MAOIs and occasionally with antipsychotics, anxiolytics and lithium
Education
Patients should be warned that anti-depressants take 7-10 days to begin to work and a month before their full benefit is seen. If effective, they should be continued for 3-12 months to avoid recurrence of symptoms upon discontinuation. Some patients may experience drowsiness and should avoid driving if this occurs.
Pharmacokinetics
Nil of note.
