Echinocanadins
Examples
- Andidulafungin
- Caspofungin
- Micafungin
Indications
Echinocanadins are only active against species of Aspergillus and Candida.
Contraindications
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity
- Hepatic impairment
- Renal impairment
- Pregnancy and breast-feeding
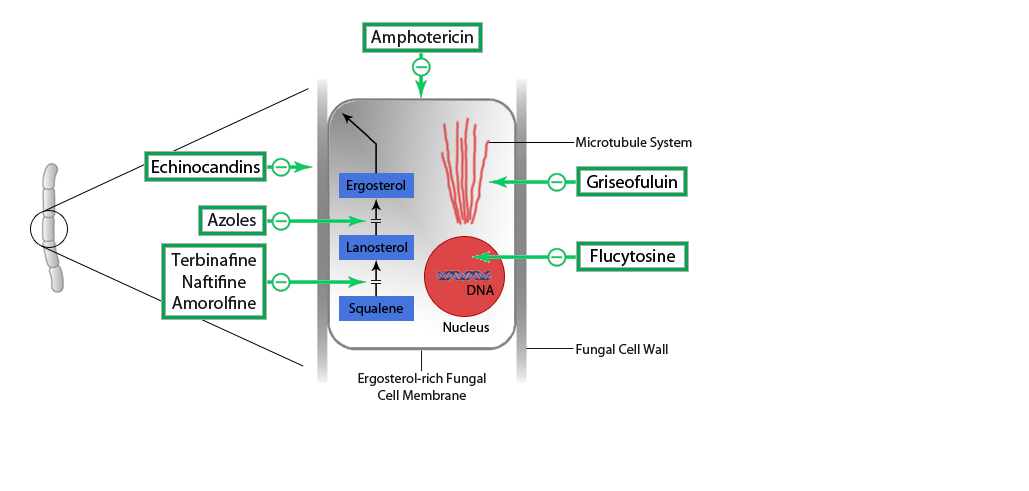
Mechanism
Echinocanadins are inhibitors of glucan synthase, an enzyme needed to produce beta (1,3)-D-glucan, an essential component for fungal cell wall stability.

Administration
Echinocandins can only be administered intravenously at present.
Adverse Reactions
Common side effects include;
- Arthralgia
- Diarrhoea
- Hypokalaemia
- Nausea and vomiting
- Rash
- Heart failure
- Liver failure
- Renal failure
Interactions
Dexamethasone, phenytoin and rifampicin all reduce caspofungin levels.
Education
Nil
Pharmacokinetics
Echinocanadins bind extensively to albumin and can take up to 2 days to distribute fully into tissue.
