Quinolones
Examples
- Ciprofloxacin
- Levofloxacin
- Moxifloxacin
Indications
- Active against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Anaerobes are resistant to the quinolones
- Ciprofloxacin is particularly active against Gram-negative bacteria, and is particularly useful in urinary sepsis, biliary tract sepsis and food poisioning
- Levofloxacin has greater activity against pneumococci than Ciprofloxacin. Moxifloxacin has greater activity against Gram-positive organisms including pneumococci than ciprofloxacin. However, these drugs are usually less useful in skin and soft tissue infections
- Although licensed, use of the quinolones should be avoided in MRSA infections
Contraindications
Contraindications
- Quinolone hypersensitivity
- History of tendon disorders related to quinolone use
- History of epilepsy or conditions that predispose to seizures
- Exposure to sunlight should be avoided and drugs discontinued if photosensitivity reactions occur
- Quinolones should be avoided in children and adolescents. Short term use of Ciprofloxacin in children is acceptable in some specific circumstances
- Pregnancy and breast-feeding
- Renal impairment
- Pre-existing history of QT interval prolongation
- Myasthenia gravis
- Elderly (more prone to tendon damage)
Mechanism
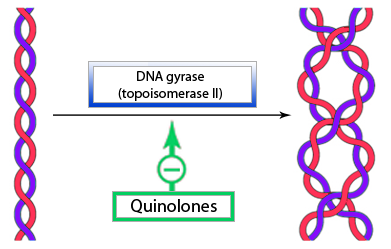
Quinolones are bactericidal drugs which act on the bacterial DNA gyrase to prevent supercoiling in the chromosome, thereby inhibiting DNA replication. Failure of the DNA to replicate prohibits transcription and replication.
Administration
- Ciprofloxacin - Oral, I.V.
- Levofloxacin - Oral, I.V.
- Moxifloxacin - Oral, I.V.
Adverse Reactions
- Common adverse effects include: Nausea and vomiting, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, diarrhoea
- A hypersensitivity rash is seen in about 1% of patients
- CNS effects such as seizures, confusion and hallucinations can occur
- LFTs abnormalities are seen
- A rare though important risk of tendon rupture exists, particularly in the elderly or patients on corticosteroids
- Quinolones (particularly ciprofloxacin) can promote C. Difficile infection.
- Can cause QT prolongation.
Interactions
- Quinolones interact with a number of drugs, by inhibiting the liver cytochrome P450 enzyme system. This is important for warfarin, phenytoin and other anti-convulsant drugs, theophylline. Always consult the BNF prior to prescribing
- Long QT syndrome can be seen when quinolones are used with anti-arrhythmics such as amiodarone, certain anti-histamines and macrolide antibiotics (particularly moxifloxacin)
- Quinolone use with ciclosporins can increase the risk of nephrotoxicity
- Quinolones and NSAIDs in combination can increase the risk of seizures
- Aluminium and magnesium antacids interfere with the absorption of quinolones
- Concomitant use of corticosteroids and quinolones can increase the risk of tendon damage occurring.
- Ciprofloxacin potentially increases the risk of toxicity when given with methotrexate.
Education
Patients should be advised to complete the prescribed course of antibiotic therapy.
Pharmacokinetics
Quinolones are well absorbed when given orally. They accumulate in a number of tissues, particularly the kidney, the prostate and the lung. Elimination by hepatic metabolism is partly via the P450 enzyme and partly by renal excretion. Doses may need adjustment in renal impairment.
