Aminoglycosides
Examples
- Gentamicin
- Amikacin
- Neomycin
- Tobramycin
Indications
- Gram negative bacteria including Pseudomonas aeruginosa and some Gram positive organisms
- Inactive on anaerobes
Contraindications
Contraindications
- Myasthenia Gravis (Aminoglycosides may impair neuromuscular transmission and large doses have been responsible for transient myasthenic syndrome in patients with normal neuromuscular function)
- Renal impairment
- Neonates and infants
- Elderly patients (due to reduced renal function)
- Dose should be monitored and adjusted together with renal, auditory and vestibular function testing
Mechanism
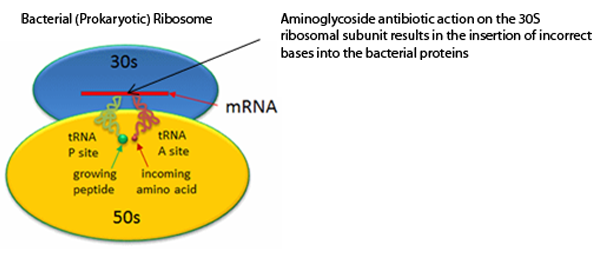
Bactericidal antibiotics which bind to the 30S subunit of the bacterial ribosome to cause misreading of the messenger RNA, leading to amino acid substitution and non-functional proteins. Penetration through the cell wall of bacterial cell membranes is by active transport, dependent on a polyamine carrier system.
Administration
- Gentamicin - I.M, I.V, Intrathecal, Intra-ocularly, Intra-aurally.
- Amikacin- I.M, I.V.
- Neomycin- Orally, Transdermally, Intraaurally.
- Tobramycin- Intraocularly, I.M, I.V, Inhalation.
Adverse Reactions
- Dose-related risk of severe nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity (vertigo or deafness)
- In large doses risk of myasthenia gravis like neuromuscular inhibition
Interactions
- Potentially ototoxic diuretics e.g. Furosemide
- Any drug which reduces renal function (e.g. NSAIDs)
- Increased risk of ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity when aminoglycosides given with vancomycin and possibly cephalosporins
- Aminoglycosides enhance the effects of non-depolarising muscle relaxants and suxamethonium
- Antibacterials inactivate the oral typhoid vaccine
Education
Patients should be advised to complete the prescribed course of antibiotic therapy.
Pharmacokinetics
Aminoglycosides are not absorbed from the gut (although there is a risk of absorption in inflammatory bowel disease and liver failure) and must therefore be given by injection for systemic infections. Excretion is principally renal and accumulation occurs in renal impairment.
