Viral Hepatisis
Hepatitis A: Overview
- RNA virus
- Usually cause acute hepatitis
- Transmitted faeco-orally
- IP: 2-3 weeks
- Serology: IgM which indicate acute infection and IgG which indicate immunity
- Cause 100% immunity after infection
Hepatitis A: Management
- Supportive: IV fluids, electrolyte correction, coagulopathy correction and symptom control
- Offer advice and vaccine for contacts
- Prevention (vaccine)
Hepatitis B Virus: Overview
- DNA virus
- Can cause both acute and chronic infection
- Transmission:
- blood borne
- IV drug abuse
- tattoos
- sexual
- vertical (mother to child)
- needle stick injury
- IP:1-6 month
Hepatitis B: Management
- Anti-viral: pegylated interferon alpha or nucleotide analogue
- Vaccination for people who are at risk
- Regular monitoring and follow up of patients
- High risk of hepatocellular cancer
Hepatitis C Virus: Overview
- RNA virus
- IP: 14-180 days
- Blood borne virus
- Currently there are no available vaccine
Hepatitis C: Management
- In patient with acute hepatitis C pegylated interferon can be used to reduce development to chronic infection
- Pegylated interferon, proteases inhibitors and ribavirin rebetol could be used in chronic infection
Hepatitis D Virus: Overview
- RNA virus, requires co-infection with HBVsAg
- Blood borne transmission
- Simultaneous infection usually cause severe form infection
Hepatitis E Virus: Overview
- Small RNA virus
- Transmitted faeco-oraly
- Usually self-limiting however rarely can cause fulminant hepatic failure specially in pregnant ladies in developing countries
- Serology: IGM , IGg. ( ELISA test for HEV Rna)
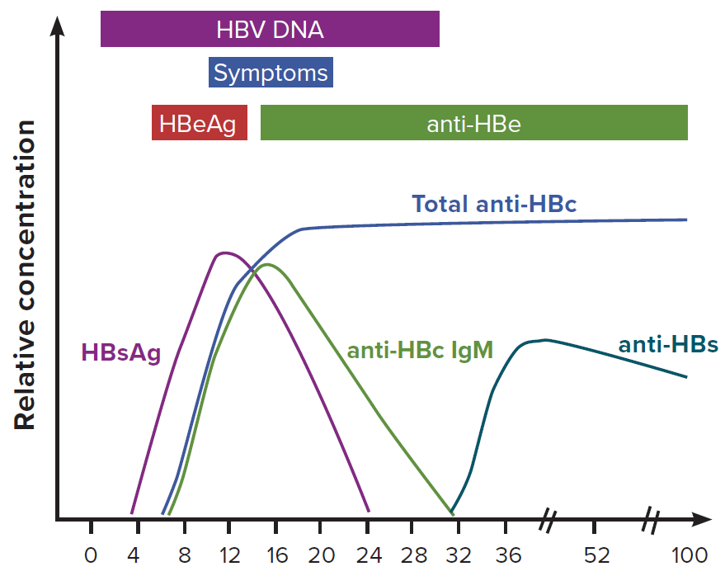
Serology
