Complement Cascade Pathways
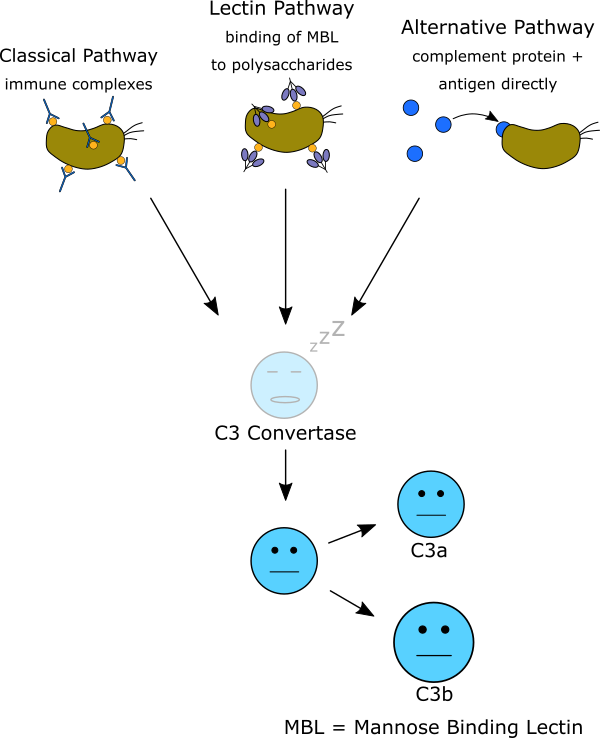
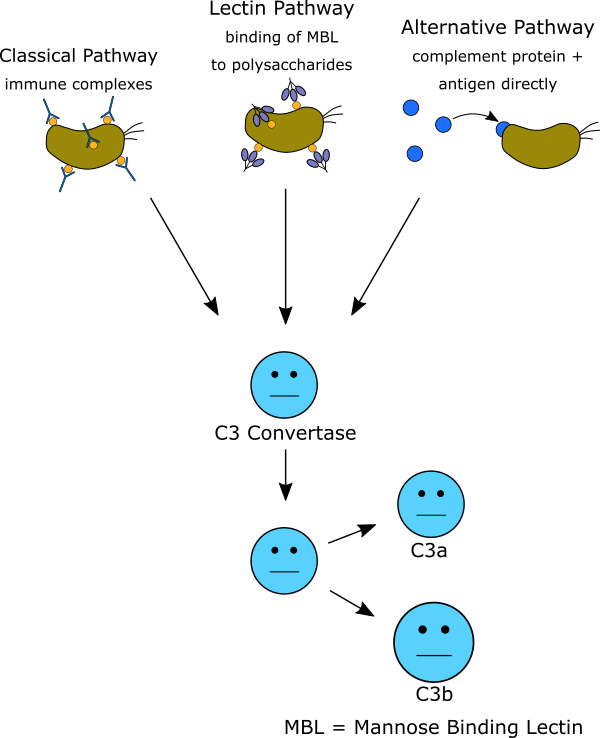
The complement cascade can be initiated, or activated, via three different pathways; the classical pathway, the lectin pathway, and the alternative pathway. The classical pathway is activated by immune complexes. The alternative pathway is activated by the direct binding of complement proteins to a pathogen. The lectin pathway is activated by the binding of microbial polysaccharides, like mannose, to circulating lectins, such as mannose binding lectin. Activation of all three of the pathways leads to the formation of C3 convertase by the amalgamation of various complement proteins. Once C3 convertase is activated, a common pathway of downstream complement effects and functions are initiated.