Nevi
Nevi (singular nevus), more commonly known as moles, are observed in most healthy skin and are more common in those with white skin
They are highly coloured (from light brown to black) small collections of highly pigmented melanocytes within the dermis
They can be present at birth or can newly appear in the skin of younger people
Please click the buttons below to learn about each type of nevi:


Figure 4. Examples of Melanocytic nevi
Melanocytic nevi
- Melanocytic nevi are collections of highly pigmented melanocytes within the dermis
- These types of moles vary in colour in different skin tones (usually brown-black) and are easier to see on pale skin
- Some moles are present at birth or appear within the first two years of life and these are known as congenital melanocytic nevi
- Moles can continue to appear in the skin of people up to around 30-40 years of age (acquired melanocytic nevi)
- Thereafter, all new moles need to be checked and monitored
- Melanocytic nevi can be found on any part of the body and can be flat or elevated
- They can vary in colour from fleshy/pink to dark brown, blue or black
- They are predominantly round or oval in shape but they can also be irregular
- They are usually small (less than 5mm in diameter) but can reach a few centimetres in diameter
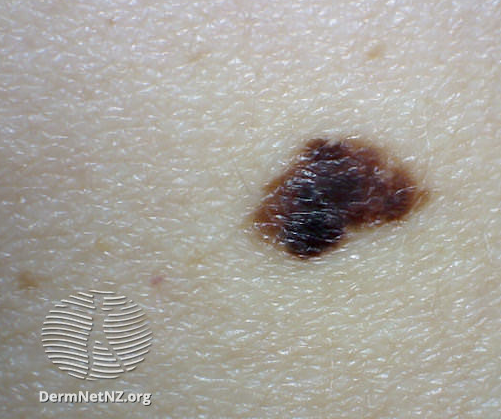
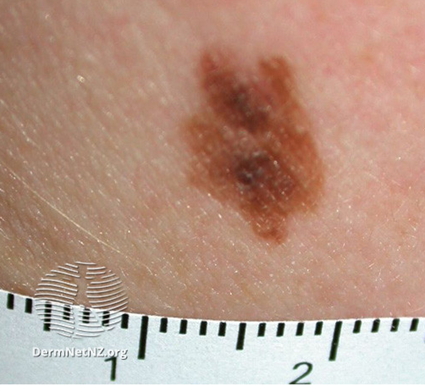
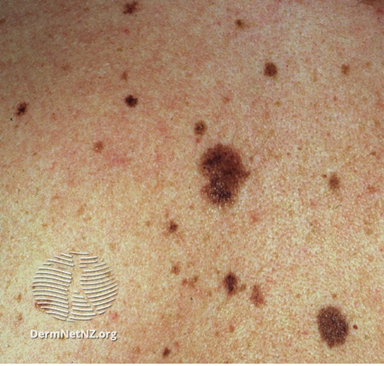
Figure 5. Examples of Dysplastic nevi
Dysplastic nevi
- Dysplastic (or atypical) nevi are benign moles but with the capacity to transform to the dangerous skin cancer cutaneous melanoma
- They have some different features but can be hard to distinguish from simple nevi
- They are usually longer than 5mm in diameter
- They usually appear as flat, slightly raised plaques, with a pebbly/ slightly scaly surface
- They can also appear as target-like lesions with a darker raised centre and irregular borders
- A dysplastic nevus can range in colour from pink to dark brown
- Dysplastic nevi can be found in almost any area of the body
- Its important to note that not all dysplastic nevi will transform to melanoma
- It can also be hard to distinguish dysplastic and simple nevi on routine inspection
- It is essential for patients to know that any pigmented lesion, anywhere on the skin which is changing should be brought to medical attention
- Some changes for which people with any pigmented nevi should seek medical advice include:
- Changes in colour
- Changes in size
- Changes in shape, texture or height
- Changes of the skin surface
- It becomes hard or lumpy
- It starts to itch
- It starts to bleed or ooze
