Introduction to The Skin
These following pages provide you with some background information about the purpose of skin and how it is made-up
There will also be examples of some benign and malignant lesions
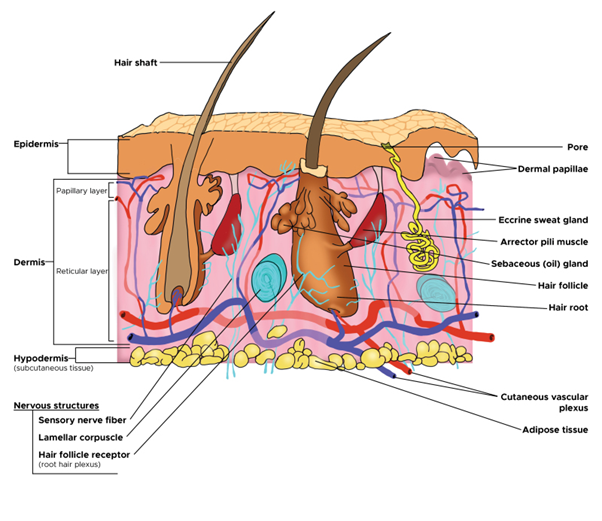
Figure 1. Basic structure of the skin
The skin is the largest organ of the body
It plays an important role in thermoregulation (maintaining the a steady temperature) and also protects the body from environmental insults such as infective pathogens (bacteria and viruses), UV light from the sun and mechanical injury
Figure 1 shows the basic structure of the skin and its constituent components
The skin consists of three layers:
- [1] the epidermis (the outer layer),
- [2] the dermis (the inner layer) and the
- [3] the hypodermis (subcutaneous fat layer)
- The epidermis and dermis layers are separated by a membrane called basal lamina
The subcutaneous fat layer, which consists of loose connective tissue and adipose tissue, binds the dermis to the underlying tissues and supports the nerves and blood vessels that come from the underlying tissues to the dermis
