AB2.H1.2 +D1 +D2 Oral Cavity and Tongue
Oral Cavity and Tongue:
Questions:
Answer Submitted
Epithelial Covering of Tongue:
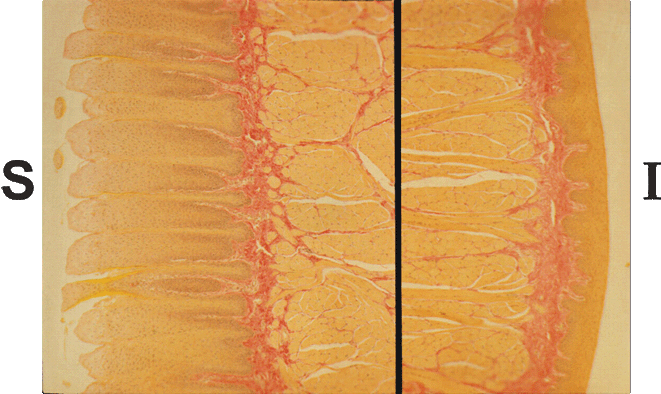
- This composite image shows the epithelial covering on the superior (S) and inferior (I) surfaces of the tongue
- The tongue and oral cavity are covered with a stratified, squamous non keratinizing epithelium
- However, notice that the epithelial covering of the superior surface of the tongue (the surface you lick with) is much thicker than the epithelium found on the inferior surface
- Also note the smooth outer surface on the inferior side of the tongue, whereas the superior (licking) side is roughened
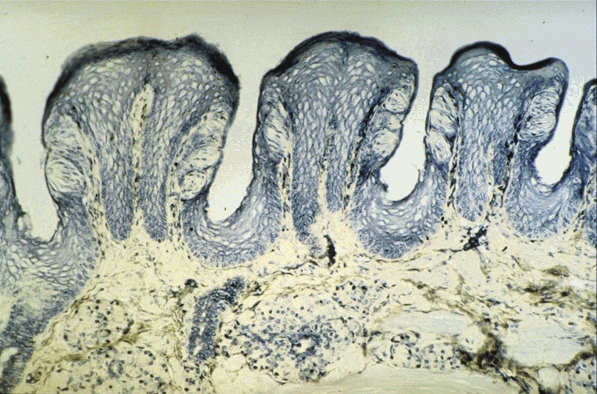
Micrograph of Papillae of the Tongue:
- This micrograph shows papillae that project from the superior surface of the tongue
- The pale ovoid cellular structures in the side wall of the papillae are taste buds