AB1.H1.5 +D1 The Gall Bladder
Accessory Glands of GI Tract:
- The gall bladder is a muscular bag which stores the bile that is produced by the liver
- Bile is an emulsifier of fats and functions in the duodenum
- When fats are detected in the duodenum the gall bladder is stimulated to contract and deliver the stored bile, via the biliary tree, into the duodenum
- The gall bladder is lined by a simple columnar epithelium sitting on a thin layer of loose connective tissue (the lamina propria)
- There is no submucosa
- There is a thin layer of smooth muscle with the muscle cells organised in different planes
- When the muscle contracts, the lumen of the gall bladder is reduced and bile is pushed into the biliary ducts where it is directed to the duodenum
- Part of the gall bladder has an adventitia which binds it to the liver
- Some parts are covered with a serosa (peritoneum)
- The tubes of the biliary tree are lined by a simple columnar epithelium supported by connective tissue
- There is a thin muscular layer in the wall of the ducts although in some parts it is thickened to form sphincters which control the direction of flow of the bile
Questions:
Answer Submitted
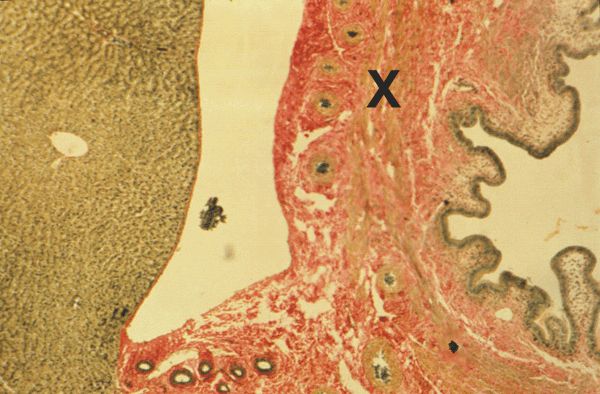
Micrograph of Gall Bladder:
- This low magnification micrograph shows an area of liver on the left and part of the gall bladder on the right
- The lumen of the gall bladder is lined by a simple columnar epithelium
- The wall of the gall bladder is muscular
- The gall bladder stores bile, when bile is required the muscle wall contracts to push stored bile out
- External to the muscle of the gall bladder wall, part of the gall bladder is covered with a serosa and part with an adventitia