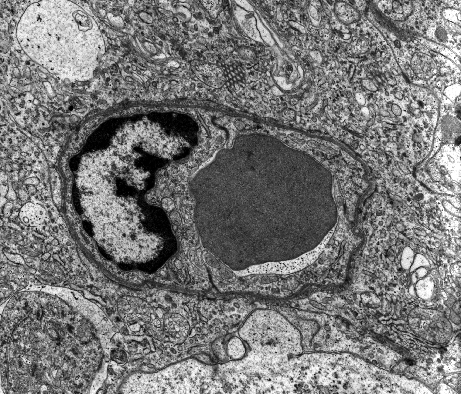
TH1.H1.5 +D1 Continuous Capillary
Capillaries:
- The capillaries are the smallest of the blood vessels in the body
- They have only a tunica intima - that is an epithelium resting on a basement membrane
- Generally the epithelium is a simple squamous type, as lines the lumina of most other parts of the cardiovascular system
- These are the blood vessels for gaseous exchange between the blood and the tissue of the body
- The exchange of proteins and other molecules as well as blood cells may also occur across capillary walls
- Continuous
- This is the most common type
- It is found where there is a need to restrict the passage of molecules, other then oxygen and carbon dioxide, across the capillary wall
- Cell junctions bind the adjacent epithelial cells
- Proteins and other molecules may cross this type of capillary, either through or between the lining epithelial cells
- However, as the lining of these capillaries is "continuous" the passage of molecules across the epithelium is controlled by the epithelial cells
- Fenestrated
- This type of capillary has fenestrations (or pores) in the epithelial cells lining the lumen
- These fenestrations will allow large molecules, including proteins to cross
- This type of capillary is common in endocrine glands
- Discontinuous
- This type of capillary has gaps between the cells which form the capillary wall
- The basement membrane is also incomplete
- In this type of capillary, unrestricted passage of fluid and proteins may occur across the capillary wall; blood cells may also cross the capillary wall
- This type of capillary is found in the bone marrow and spleen
Three types of capillary are found:
Micrograph of Continuous Capillary:
Question:
Answer Submitted