LL1.H1.1a +b+c+d+e Connective Tissue Types
Peripheral blood:
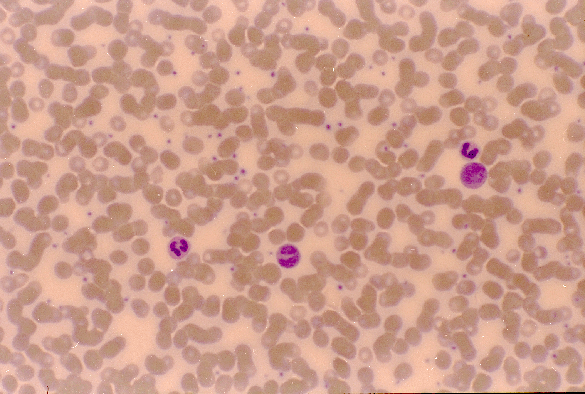
- Peripheral blood is a kind of connective tissue where the extracellular matrix is fluid
Bone Marrow:
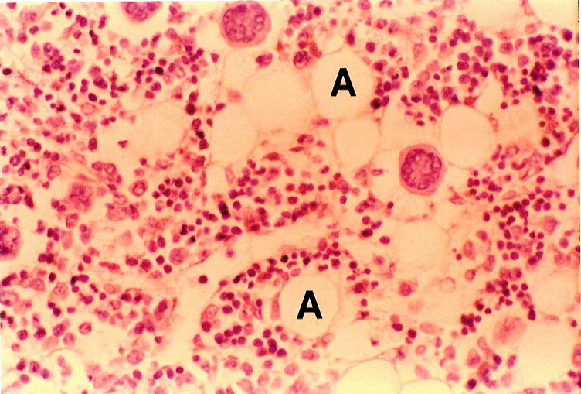
- Bone marrow is a type of connective tissue with a loose framework of fine reticular cells and reticular fibres which support the haematopoetic cells
- Bone marrow also contains some adipose cells (A)
- Superficial fascia and other fat deposits in the body consist of a large mass of adipose cells and blood vessels
- Why are the blood vessels present?
Reticular Connective Tissue:
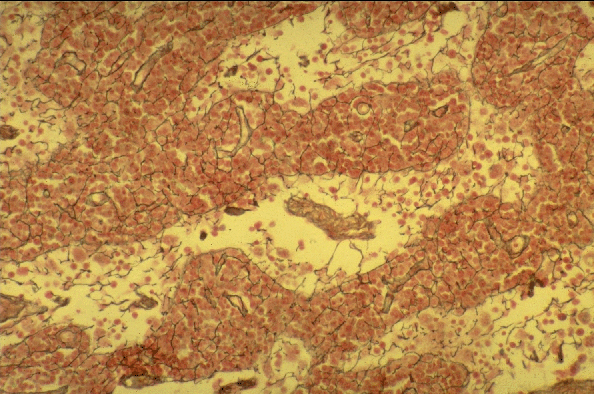
- This micrograph shows part of a lymph node
- Fine reticular cells and reticular fibres (stained black in this preparation) form the reticular connective tissue that supports the lymphoid cells of the lymph node
Loose Connective Tissue: 1
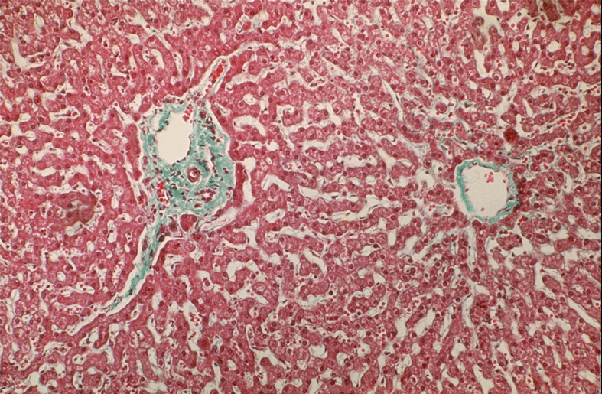
- In the liver, loose connective tissue (shown in green on this micrograph) supports the larger (bile) ducts and blood vessels that permeate this viscus
Loose Connective Tissue: 2
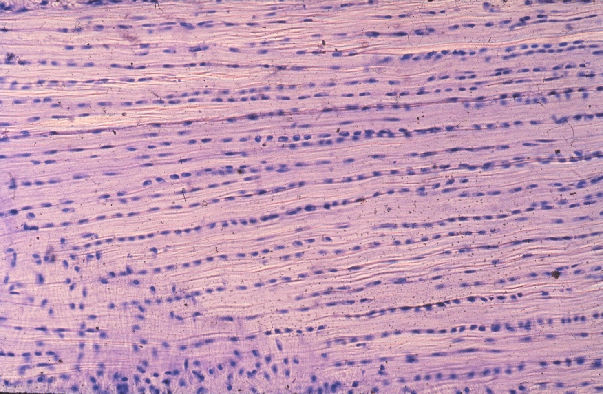
- This micrograph shows fibroblasts with thick bundles of collagen in extracellular space between
- Note that in dense regular connective tissue the cells and bundles of collagen are organised in rows and running in the same direction
- This type of connective tissue is found in ligaments and tendons
- In a long tendon, would these rows of cells and collagen bundles be lying along the long axis of the tendon or at 90 degrees to the long axis of the tendon? Why?
