B7 +D1 +D2 Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes:
- Lymphocytes are found as two (morphological) types: small and medium
- Lymphocytes are a type of agranular leucocyte although some types of lymphocytes do contain very small cytoplasmic granules which are functionally important
- Lymphocytes are cells which are central to the functioning of the immune system
- Functionally, it is now known that there are many different types of lymphocyte (T, B, NK etc). These cannot be distinguished morphologically
- However, they can routinely be classified according to the surface expression of specific proteins which can be identified using labelled antibodies (immunocytochemistry)
- Small lymphocytes are about 8-9 microns in diameter ie about the size of a red blood cell
- In a Romanovsky-type stained peripheral blood smear they appear as a round cell with a heterochromatic nucleus and little discernible cytoplasm
- Medium lymphocytes are about 1O-12 microns in diameter and have a larger more euchromatic nucleus than small lymphocytes
- They also have more cytoplasm
- Medium lymphocytes are now more usually classified as activated lymphocytes because it is recognized that they arise from small lymphocytes as part of an immune response
- Lymphocytes represent about 20-40% of white blood cells in normal circulating blood
- The time these cells spend in the blood, and in tissue spaces, is highly variable largely depending on sub-type and function
Lymphocytes - 2:
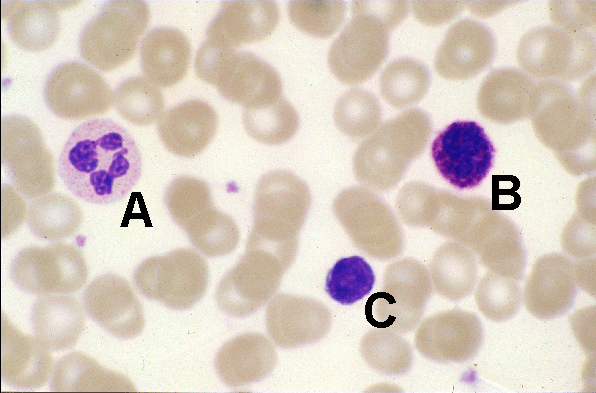
- In this image of a blood smear a small lymphocyte is labelled C (A = neutrophil, B = basophil)
- The nucleus of the small lymphocyte appears to occupy the whole cell but if you look closely at the top edge of the cell you can see a small amount of cytoplasm
- The small lymphocyte has a similar diameter to surrounding red blood cells but has a smaller diameter than the neutrophil and basophil also shown on this image
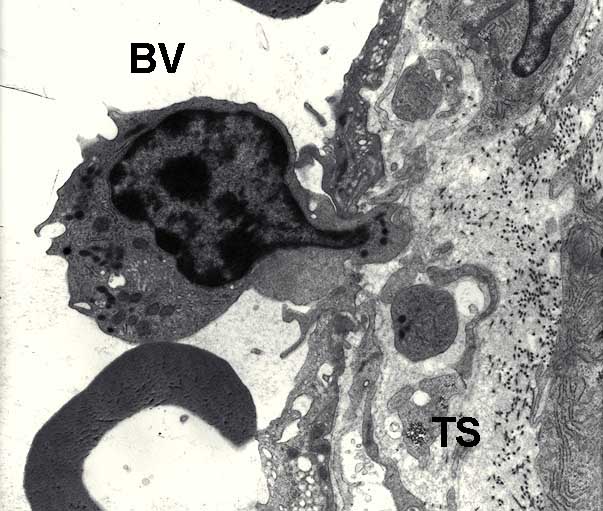
Lymphocytes - 3:
- In this electron micrograph a medium (activated) lymphocyte is shown
- By comparison with a small lymphocyte, the medium lymphocyte is larger, has a larger more euchromatic nucleus and a fair amount of cytoplasm
- In this example, the lymphocyte appears to be passing between endothelial cells of the thin walled blood vessels (BV) into (probably?) tissue space (TS)