- VC1.H1.1 Histology of the Spinal Cord
- VC1.H1.2 Spinal Cord
- VC1.H1.3 +D1 +D2 White Matter
- VC1.H1.4 Grey Matter
- VC1.H1.5 Dorsal Root Ganglion
- VC1.H1.6 +D1 +D2 Peripheral Nerve
- VC1.H1.7 and INT.H1.8 Sensory Receptors
- VC1.H2.1 Histology of the Skin
- VC1.H2.2 Skin Thickness
- VC1.H2.3 +4 Thin Skin and Thick Skin
- VC1.H2.5 Sensory Receptors
- VC1.H2.6 +7 Meissner's and Paccinian Corpuscle
- UL1.H1.1 Muscle Tissue
- UL1.H1.2 Smooth and Cardiac Muscle
- UL1.H1.2D1 Cardiac Muscle
- UL1.H1.3 Smooth Muscle Organisation
- UL1.H1.3D1 Smooth Muscle
- UL1.H1.4 +D1 Skeletal Muscle
- UL1.H1.5 +D1 Skeletal Muscle Organisation
- UL1.H1.6 +D1 Orientation of Skeletal Muscle Cells
- UL1.H1.6a +b+c+d Muscles Examples
- UL1.H1.7 +a Motor Units
- UL2.H1.1 +D1 Bone
- UL2.H1.2 +D1 +D2 Bone Cells
- UL2.H1.3 +D1 +D2 Compact Bone
- UL2.H1.4 Cancellous Bone
- UL2.H1.5 +D1 Periosteum
- LL1.H1.1 Connective Tissue
- LL1.H1.1a +b+c+d+e Connective Tissue Types
- LL1.H1.2 Loose Connective Tissue
- LL1.H1.3 Dense Connective Tissue
- LL1.H1.4 Superficial and Deep Fascia
- LL1.H1.5 +D1 Connective Tissue around Muscle
- LL1.H1.6 Tendons and Ligaments
- LL1.H1.7 +D1 Muscle, Tendon, Bone Connections
- LL1.H1.8 +D1 Ligament - Bone Connections
- TH1.H1.1 Histology of Heart and Blood Vessel Walls
- TH1.H1.2 Histology of Heart and Blood Vessel Walls
- TH1.H1.2D1 Cardiac Muscle Cells
- TH1.H1.2D2 Cardiac Muscle Cells
- TH1.H1.3 Arteries
- TH1.H1.3D1 Muscular Artery
- TH1.H1.3D2 Helicine Artery of Penis
- TH1.H1.4 +D1 Arterioles
- TH1.H1.5 +D1 Continuous Capillary
- TH1.H1.5D2 Fenestrated Capillary
- TH1.H1.6 Veins, +D1 Peripheral Veins
- TH1.H1.7 Valves
- TH1.H2.1 +D1 Histology of the Upper Respiratory Tract
- TH1.H2.2 +D1 Trachea and Extrapulmonary Bronchi
- TH1.H2.2D2 Trachea and Extrapulmonary Bronchi
- TH1.H2.2D3 +D4 Trachea and Extrapulmonary Bronchi
- TH1.H2.3 +D1 Bronchial tree
- TH1.H2.4 +D1 Alveoli
- TH1.H2.5 Alveoli Walls
- TH1.H2.6 +D1 Elastic Tissue in Lungs
- AB1.H1.1 Plan of Gut Tube
- AB1.H1.2 +D1 +D2 Accessory Glands of GI Tract, Goblet Cells, Submucosal Gland
- AB1.H1.3 +D1 Liver Organisation
- AB1.H1.3D3 Liver Organisation
- AB1.H1.3D4 Liver Organisation
- AB1.H1.4 The Liver - Hepatocytes
- AB1.H1.5 +D1 The Gall Bladder
- AB1.H1.6 +D1 The Pancreas
- AB2.H1.2 +D1 +D2 Oral Cavity and Tongue
- AB2.H1.3 Oesophagus
- AB2.H1.4 Stomach
- AB2.H1.5 Small Intestine
- AB2.H1.5D1 Villi
- AB2.H1.5D2 Brunner's Glands
- AB2.H1.6 +D1 Large Intestine
- AB2.H1.7 Appendix
- AB2.H1.8 Anal Canal
- AB2.H1.9 +D1 Cell Turnover
- AB2.H1.10 Area for Absorption
- PP1.H1.1 +D1 The Urinary System - Kidney
- PP1.H1.2 +D1 The kidney
- PP1.H1.3 +D1 The nephron
- PP1.H1.4 +D1 +D2 +D3 The Renal Corpuscle
- PP1.H1.5 +D1 +D2 The Filtration Barrier
- PP1.H1.6 +D1 +D2 Kidney Tubules
- PP1.H1.7 +D1 Collecting Ducts and the Renal Pelvis
- PP1.H1.8 Blood Vessels of Kidney
- PP2.H1.1 The Urinary System - Extra-Renal Components
- PP1.H2.2 The Ureter
- PP1.H2.3 The Urinary Bladder
- PP1.H2.4 Transitional Epithelium
- PP1.H2.5 The Urethra
- PP2.H1.1 +D1 The Male Genital System
- PP2.H1.2 +D1 The Testis
- PP2.H1.3 +D1 Seminiferous Tubules
- PP2.H1.4 Interstitial Cells of Leydig
- PP2.H1.5 +D1 The Mediastinum Testis
- PP2.H1.6 +D1 The Ductuli Efferentes
- PP2.H1.7 +D1 The Epididymis
- PP2.H1.8 +D1 The Ductus Deferens and The Ejaculatory Duct
- PP2.H1.9 +D1 The Penis
- PP2.H1.10 +D1 Seminal Vesicles
- PP2.H1.11 +D1 The Prostate
- PP2.H2.1 +D1 The Female Reproductive System
- PP2.H2.2 The Menstrual Cycle
- PP2.H2.3 +D1 Ovary
- PP2.H2.4 Ovarian Follicles 1
- PP2.H2.5 Ovarian Follicles 2
- PP2.H2.6 +D1 Primordial and Primary Ovarian Follicles
- PP2.H2.7 +D1 +D2 Secondary Ovarian Follicles
- PP2.H2.8 +D1 Graafian Follicles
- PP2.H2.9 +D1 Corpus Luteum
- PP2.H2.10 +D1 Atretic Follicles and Corpora Albicantes
- HN1.H1.1 Salivary Glands - General
- HN1.H1.2 +D1 Parotid Gland
- HN1.H1.3 +D1 Submandibular Gland
- HN1.H1.4 +D1 Sublingual Gland
- HN1.H1.5 +D1 Oesophageal Glands
- HN2.H1.1 Oral Cavity and Tongue
- HN2.H1.2 +D1 Tongue - Dorsal Surface Epithelium
- HN2.H1.3 +D1 Tongue - Ventral Surface Epithelium
- HN2.H1.4 +D1 Tongue Muscle Groups
- HN2.H1.5 Tongue - Salivary Glands
- HN2.H1.6 +D1 Taste Buds
- HN3.H1.1 +D1 +D2 The Thyroid Gland
- HN3.H1.1D3 Fenestrated Capillaries
- HN3.H1.2 +D1 +D2 The Parathyroid Glands
- HN3.H1.3 +D1 The Pituitary Gland - Development
- HN3.H1.4 +D1 +D2 +D3 The Anterior Pituitary
- HN3.H1.5 +D1 +D1 The Posterior Pituitary
- HN3.H1.6 The Blood Vessels of The Pituitary Gland
- HN3.H1.7 +D1 The Hypophysioportal Circulation
- HN3.H1.8 +D1 +D2 Tonsils
- HP0 Primary Tissues
- HP1 Epithelia Classification
- HP2.1 Epithelia Functions: Absorbtion of nutrients?
- HP2.2 Epithelia Functions: Movement of mucus/other material across a surface?
- HP2.3 Epithelia Functions: Resistance to chemical attack?
- HP2.4 Epithelia Functions: Diffusion of substances across an epithelial layer?
- HP2.5 Epithelia Functions: Wear and Tear?
- HP2.6 Epithelia Functions: Stretchability?
- HP3 Secretion
- HP4 Passage Across Epithelium
- HP4a Passage Across Epithelium 1
- HP4b Passage Across Epithelium 2
- HP5 Glands
- HP6 Unicellular Glands
- HP7 Endocrine Gland
- HP8 Ciliated Epithelium
Contents
Preface
Nervous System
Skin 1
Bone
Cartilage
Connective Tissue
Skin 2
Cardiovascular
Respiratory
Breast
Accessory Glands of GI Tract
GI Tract
Lymphoid Tissue
Urinary - Kidney
Urinary Extra-Renal
The Male Genital System
Female Reproductive 1
Female Reproductive 2
Salivary Glands
Oral Cavity
Endocrine Glands
The Blood
Histology Practicals
a-short-review-of-histology
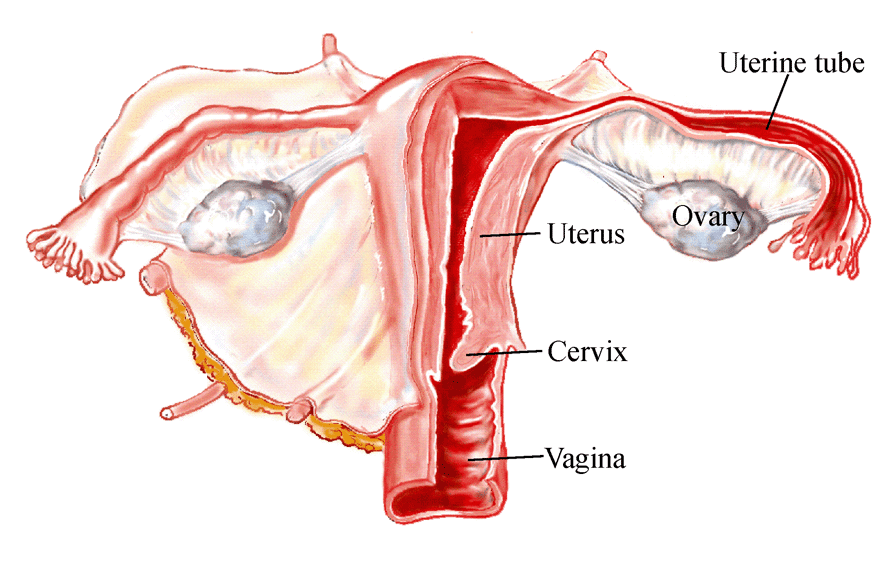
PP2.H2.1 +D1 The Female Reproductive System
The Female Reproductive System:
- The female reproductive system consists of:
- Ovaries (paired) - release ova for fertilisation and produce hormones which stimulate other parts of the female reproductive tract and support pregnancy
- Uterine tubes (paired) - Provide an environment to support the ovum during fertilisation and delivery of the zygote to the uterus
- Uterus (single) - provides an environment to support embryo development
- Vagina (single) - receives the male-sex organ (penis) and the seminal fluid
- External genitalia
- The structure and function of the female reproductive system is influenced by hormones
- The hormonal milieu is found in three phase during an individual's life:
- Prepubertal phase - the structural components of the female reproductive system are present but not stimulated to allow reproduction
- Reproductive phase - the female reproductive system is actively able to support the development of an embryo and foetus Its structure and function changes on a cyclical basis, influenced by hormones of the menstrual cycle
- Post menopausal phase - reproductive capacity is exhausted and the components of the female reproductive tract cease to be stimulated by hormones of reproduction and atrophy
Diagram of Female Reproductive System: