- VC1.H1.1 Histology of the Spinal Cord
- VC1.H1.2 Spinal Cord
- VC1.H1.3 +D1 +D2 White Matter
- VC1.H1.4 Grey Matter
- VC1.H1.5 Dorsal Root Ganglion
- VC1.H1.6 +D1 +D2 Peripheral Nerve
- VC1.H1.7 and INT.H1.8 Sensory Receptors
- VC1.H2.1 Histology of the Skin
- VC1.H2.2 Skin Thickness
- VC1.H2.3 +4 Thin Skin and Thick Skin
- VC1.H2.5 Sensory Receptors
- VC1.H2.6 +7 Meissner's and Paccinian Corpuscle
- UL1.H1.1 Muscle Tissue
- UL1.H1.2 Smooth and Cardiac Muscle
- UL1.H1.2D1 Cardiac Muscle
- UL1.H1.3 Smooth Muscle Organisation
- UL1.H1.3D1 Smooth Muscle
- UL1.H1.4 +D1 Skeletal Muscle
- UL1.H1.5 +D1 Skeletal Muscle Organisation
- UL1.H1.6 +D1 Orientation of Skeletal Muscle Cells
- UL1.H1.6a +b+c+d Muscles Examples
- UL1.H1.7 +a Motor Units
- UL2.H1.1 +D1 Bone
- UL2.H1.2 +D1 +D2 Bone Cells
- UL2.H1.3 +D1 +D2 Compact Bone
- UL2.H1.4 Cancellous Bone
- UL2.H1.5 +D1 Periosteum
- LL1.H1.1 Connective Tissue
- LL1.H1.1a +b+c+d+e Connective Tissue Types
- LL1.H1.2 Loose Connective Tissue
- LL1.H1.3 Dense Connective Tissue
- LL1.H1.4 Superficial and Deep Fascia
- LL1.H1.5 +D1 Connective Tissue around Muscle
- LL1.H1.6 Tendons and Ligaments
- LL1.H1.7 +D1 Muscle, Tendon, Bone Connections
- LL1.H1.8 +D1 Ligament - Bone Connections
- TH1.H1.1 Histology of Heart and Blood Vessel Walls
- TH1.H1.2 Histology of Heart and Blood Vessel Walls
- TH1.H1.2D1 Cardiac Muscle Cells
- TH1.H1.2D2 Cardiac Muscle Cells
- TH1.H1.3 Arteries
- TH1.H1.3D1 Muscular Artery
- TH1.H1.3D2 Helicine Artery of Penis
- TH1.H1.4 +D1 Arterioles
- TH1.H1.5 +D1 Continuous Capillary
- TH1.H1.5D2 Fenestrated Capillary
- TH1.H1.6 Veins, +D1 Peripheral Veins
- TH1.H1.7 Valves
- TH1.H2.1 +D1 Histology of the Upper Respiratory Tract
- TH1.H2.2 +D1 Trachea and Extrapulmonary Bronchi
- TH1.H2.2D2 Trachea and Extrapulmonary Bronchi
- TH1.H2.2D3 +D4 Trachea and Extrapulmonary Bronchi
- TH1.H2.3 +D1 Bronchial tree
- TH1.H2.4 +D1 Alveoli
- TH1.H2.5 Alveoli Walls
- TH1.H2.6 +D1 Elastic Tissue in Lungs
- AB1.H1.1 Plan of Gut Tube
- AB1.H1.2 +D1 +D2 Accessory Glands of GI Tract, Goblet Cells, Submucosal Gland
- AB1.H1.3 +D1 Liver Organisation
- AB1.H1.3D3 Liver Organisation
- AB1.H1.3D4 Liver Organisation
- AB1.H1.4 The Liver - Hepatocytes
- AB1.H1.5 +D1 The Gall Bladder
- AB1.H1.6 +D1 The Pancreas
- AB2.H1.2 +D1 +D2 Oral Cavity and Tongue
- AB2.H1.3 Oesophagus
- AB2.H1.4 Stomach
- AB2.H1.5 Small Intestine
- AB2.H1.5D1 Villi
- AB2.H1.5D2 Brunner's Glands
- AB2.H1.6 +D1 Large Intestine
- AB2.H1.7 Appendix
- AB2.H1.8 Anal Canal
- AB2.H1.9 +D1 Cell Turnover
- AB2.H1.10 Area for Absorption
- PP1.H1.1 +D1 The Urinary System - Kidney
- PP1.H1.2 +D1 The kidney
- PP1.H1.3 +D1 The nephron
- PP1.H1.4 +D1 +D2 +D3 The Renal Corpuscle
- PP1.H1.5 +D1 +D2 The Filtration Barrier
- PP1.H1.6 +D1 +D2 Kidney Tubules
- PP1.H1.7 +D1 Collecting Ducts and the Renal Pelvis
- PP1.H1.8 Blood Vessels of Kidney
- PP2.H1.1 The Urinary System - Extra-Renal Components
- PP1.H2.2 The Ureter
- PP1.H2.3 The Urinary Bladder
- PP1.H2.4 Transitional Epithelium
- PP1.H2.5 The Urethra
- PP2.H1.1 +D1 The Male Genital System
- PP2.H1.2 +D1 The Testis
- PP2.H1.3 +D1 Seminiferous Tubules
- PP2.H1.4 Interstitial Cells of Leydig
- PP2.H1.5 +D1 The Mediastinum Testis
- PP2.H1.6 +D1 The Ductuli Efferentes
- PP2.H1.7 +D1 The Epididymis
- PP2.H1.8 +D1 The Ductus Deferens and The Ejaculatory Duct
- PP2.H1.9 +D1 The Penis
- PP2.H1.10 +D1 Seminal Vesicles
- PP2.H1.11 +D1 The Prostate
- PP2.H2.1 +D1 The Female Reproductive System
- PP2.H2.2 The Menstrual Cycle
- PP2.H2.3 +D1 Ovary
- PP2.H2.4 Ovarian Follicles 1
- PP2.H2.5 Ovarian Follicles 2
- PP2.H2.6 +D1 Primordial and Primary Ovarian Follicles
- PP2.H2.7 +D1 +D2 Secondary Ovarian Follicles
- PP2.H2.8 +D1 Graafian Follicles
- PP2.H2.9 +D1 Corpus Luteum
- PP2.H2.10 +D1 Atretic Follicles and Corpora Albicantes
- HN1.H1.1 Salivary Glands - General
- HN1.H1.2 +D1 Parotid Gland
- HN1.H1.3 +D1 Submandibular Gland
- HN1.H1.4 +D1 Sublingual Gland
- HN1.H1.5 +D1 Oesophageal Glands
- HN2.H1.1 Oral Cavity and Tongue
- HN2.H1.2 +D1 Tongue - Dorsal Surface Epithelium
- HN2.H1.3 +D1 Tongue - Ventral Surface Epithelium
- HN2.H1.4 +D1 Tongue Muscle Groups
- HN2.H1.5 Tongue - Salivary Glands
- HN2.H1.6 +D1 Taste Buds
- HN3.H1.1 +D1 +D2 The Thyroid Gland
- HN3.H1.1D3 Fenestrated Capillaries
- HN3.H1.2 +D1 +D2 The Parathyroid Glands
- HN3.H1.3 +D1 The Pituitary Gland - Development
- HN3.H1.4 +D1 +D2 +D3 The Anterior Pituitary
- HN3.H1.5 +D1 +D1 The Posterior Pituitary
- HN3.H1.6 The Blood Vessels of The Pituitary Gland
- HN3.H1.7 +D1 The Hypophysioportal Circulation
- HN3.H1.8 +D1 +D2 Tonsils
- HP0 Primary Tissues
- HP1 Epithelia Classification
- HP2.1 Epithelia Functions: Absorbtion of nutrients?
- HP2.2 Epithelia Functions: Movement of mucus/other material across a surface?
- HP2.3 Epithelia Functions: Resistance to chemical attack?
- HP2.4 Epithelia Functions: Diffusion of substances across an epithelial layer?
- HP2.5 Epithelia Functions: Wear and Tear?
- HP2.6 Epithelia Functions: Stretchability?
- HP3 Secretion
- HP4 Passage Across Epithelium
- HP4a Passage Across Epithelium 1
- HP4b Passage Across Epithelium 2
- HP5 Glands
- HP6 Unicellular Glands
- HP7 Endocrine Gland
- HP8 Ciliated Epithelium
Contents
Preface
Nervous System
Skin 1
Bone
Cartilage
Connective Tissue
Skin 2
Cardiovascular
Respiratory
Breast
Accessory Glands of GI Tract
GI Tract
Lymphoid Tissue
Urinary - Kidney
Urinary Extra-Renal
The Male Genital System
Female Reproductive 1
Female Reproductive 2
Salivary Glands
Oral Cavity
Endocrine Glands
The Blood
Histology Practicals
a-short-review-of-histology
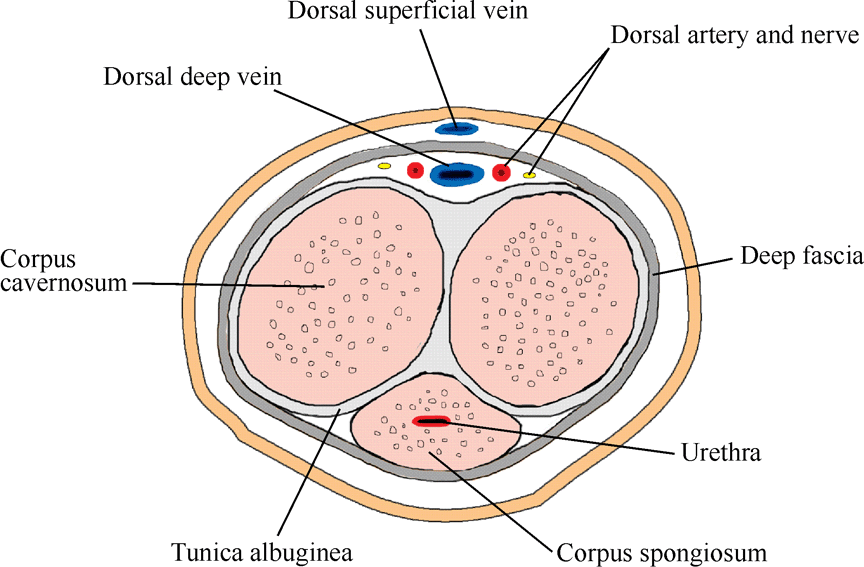
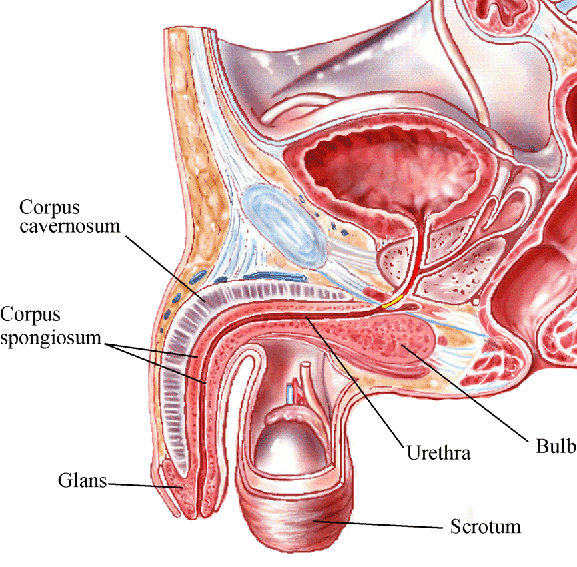
PP2.H1.9 +D1 The Penis
The Penis:
- The penis consists of three cylindrical bodies of erectile tissue
- They are known as cavernous bodies
- Each cavernous body is enclosed within a dense connective tissue sheath
- The cavernous bodies are held together by connective tissue containing elastic fibres, overlain with thin skin
- Each cavernous body consists of endothelial lined spaces between connective tissue trabeculae
- The penis contains numerous sensory receptors associated with sexual arousal as well as a rich motor nerve supply to control the mechanism of erection
- Helicine arteries, with both circular and longitudinal layers of smooth muscle cells in their walls, supply blood to the vascular spaces of the cavernous bodies
- Parasympathetic nerves stimulate dilatation of the helicine arteries to allow blood to flow into the vascular spaces and cause erection
- The resting tone (sympathetic control) of the muscular walls of the helicine arteries causes constriction of the helicine arteries and prevents blood flow into the vascular spaces to maintain the penis in a flaccid state
Diagrams of The Penis: