PP1.H1.5 +D1 +D2 The Filtration Barrier
The Filtration Barrier:
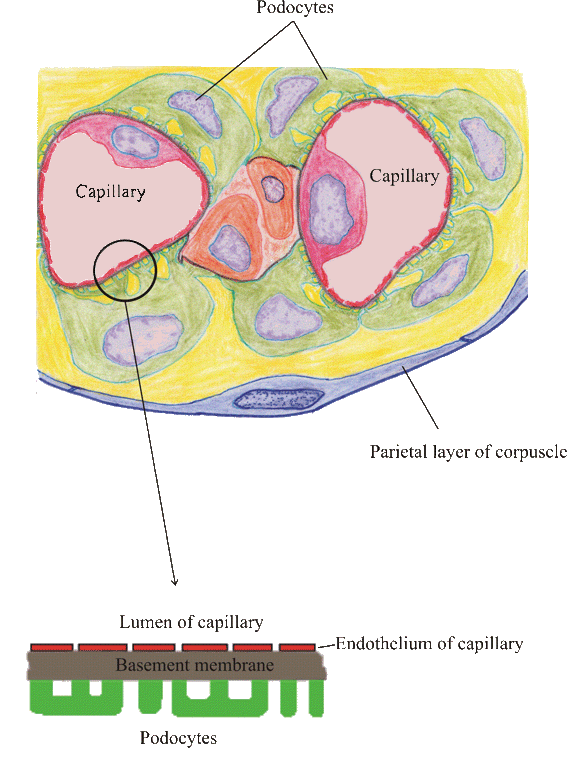
- The association between the visceral layer of the Bowman's capsule and the capillary walls of the glomerulus, together with their respective basement membranes form a filtration barrier across which the blood is filtered
- This barrier has three layers:
- The endothelium of the capillary
- The capillaries of the glomerulus are highly fenestrated
- These fenestrations act as a coarse filter to prevent the passage of blood cells including platelets
- Basement membrane
- The basement membrane of the filtration barrier is relatively thick and is formed by the fusion of the basement membrane from the capillary epithelium as well as the visceral layer of the Bowman's capsule
- This is the main filtration barrier and prevents the passage of molecules >69Kd (most proteins) or negatively charged molecules
- The cells of the visceral layer of Bowman's capsule, known as podocytes, have cytoplasmic extensions which terminate in numerous "foot processes"
- These foot processes wrap around the outside of the capillaries in an organised fashion with 20-30nm slits between them through which the filtrate will pass to enter the Bowman's space
- There is a high pressure within the lumina of the glomerular capillaries which helps the filtration process
- The foot process provide an external skeleton to the capillaries to prevent the capillaries from being blown apart by the high pressure
Diagram of Filtration Barrier:
Micrograph of Filtration Barrier:
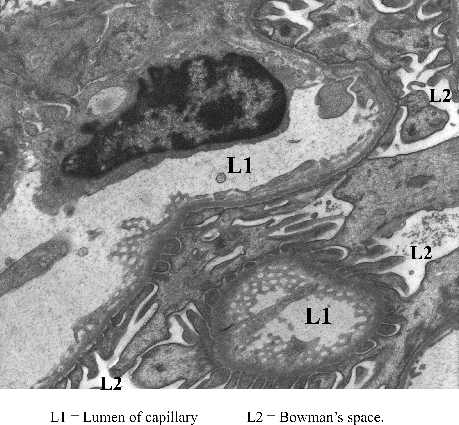
Can you identify the following?
- Fenestrated endothelium of capillary
- Basement membrane of filtration barrier
- Foot processes
